Surface-patterned electrode bioreactor for electrical stimulation
- PMID: 20221556
- PMCID: PMC3618471
- DOI: 10.1039/b917743d
Surface-patterned electrode bioreactor for electrical stimulation
Abstract
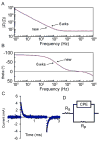
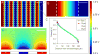
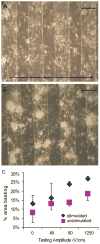
We present a microscale cell culture system with an interdigitated microarray of excimer-laser-ablated indium tin oxide electrodes for electrical stimulation of cultured cells. The system has been characterized in a range of geometeries and stimulation regimes via electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and used to culture primary cardiomyocytes and human adipose derived stem cells. Over 6 days of culture with electrical stimulation (2 ms duration, 1 Hz, 180 microm wide electrodes with 200 microm spacing), both cell types exhibited enhanced proliferation, elongation and alignment, and adipose derived stem cells exhibited higher numbers of Connexin-43-composed gap junctions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of electrical stimulation electrodes for cardiac tissue engineering.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;2006:845-8. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2006.259747. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006. PMID: 17946862
-
An electro-tensile bioreactor for 3-D culturing of cardiomyocytes. A bioreactor system that simulates the myocardium's electrical and mechanical response in vivo.IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2005 Jul-Aug;24(4):73-9. doi: 10.1109/memb.2005.1463399. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 2005. PMID: 16119216 No abstract available.
-
Design and validation of a bioreactor for simulating the cardiac niche: a system incorporating cyclic stretch, electrical stimulation, and constant perfusion.Tissue Eng Part A. 2013 Feb;19(3-4):403-14. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2012.0135. Epub 2012 Dec 10. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013. PMID: 22991978
-
Electrical and mechanical stimulation of cardiac cells and tissue constructs.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Jan 15;96:135-55. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.07.009. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26232525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue engineering bioreactor systems for applying physical and electrical stimulations to cells.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015 May;103(4):935-48. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33268. Epub 2014 Aug 29. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015. PMID: 25171208 Review.
Cited by
-
Tailoring cardiac environment in microphysiological systems: an outlook on current and perspective heart-on-chip platforms.Future Sci OA. 2017 May 3;3(2):FSO191. doi: 10.4155/fsoa-2017-0024. eCollection 2017 Jun. Future Sci OA. 2017. PMID: 28670478 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Contact photolithography-free integration of patterned and semi-transparent indium tin oxide stimulation electrodes into polydimethylsiloxane-based heart-on-a-chip devices for streamlining physiological recordings.Lab Chip. 2021 Feb 23;21(4):674-687. doi: 10.1039/d0lc00948b. Lab Chip. 2021. PMID: 33439202 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture design and advanced manufacturing of heart-on-a-chip: scaffolds, stimulation and sensors.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024 Jul 11;10:96. doi: 10.1038/s41378-024-00692-7. eCollection 2024. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024. PMID: 39006908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Cardiac Tissue Engineering for the Management of Myocardium Infarction.Cells. 2021 Sep 25;10(10):2538. doi: 10.3390/cells10102538. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic platforms for human stem cell research.Cell Stem Cell. 2011 Mar 4;8(3):252-61. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2011.02.014. Cell Stem Cell. 2011. PMID: 21362565 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

