Drug-induced QT prolongation and sudden death
- PMID: 20222297
- PMCID: PMC6192813
Drug-induced QT prolongation and sudden death
Abstract
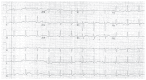
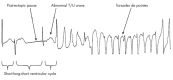
Prolongation of the QT interval can predispose to a potentially fatal polymorphic ventricular tachycardia called torsades de pointes (TdP). Although usually self-limited, TdP may degenerate into ventricular fibrillation and cause sudden death. Some medications that cause QT prolongation and possible TdP are commonly used in general practice. This paper presents a case of sudden death that is likely from drug-induced TdP. It reviews the mechanisms, risk factors, offending agents, and management of drug-induced torsades de pointes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Drugs that cause Torsades de pointes and increase the risk of sudden cardiac death.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2004 Sep;6(5):379-84. doi: 10.1007/s11886-004-0041-8. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2004. PMID: 15306095 Review.
-
[QTc-prolonging drugs and the risk of sudden death].Medicina (Kaunas). 2007;43(4):347-53. Medicina (Kaunas). 2007. PMID: 17485963 Review. Lithuanian.
-
Pharmacologic agents associated with QT interval prolongation.J Fam Pract. 2005 Jun;Suppl:S8-S14. J Fam Pract. 2005. PMID: 15938993 Review.
-
Antipsychotic-related QTc prolongation, torsade de pointes and sudden death.Drugs. 2002;62(11):1649-71. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262110-00006. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12109926 Review.
-
Reckless administration of QT interval-prolonging agents in elderly patients with drug-induced torsade de pointes.Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018 Jan;51(1):41-47. doi: 10.1007/s00391-016-1155-5. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018. PMID: 27878411 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Cirrhotic Cardiomyopathy: The Interplay Between Liver and Heart.Cureus. 2022 Aug 13;14(8):e27969. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27969. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36120195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac risks associated with antibiotics: azithromycin and levofloxacin.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2015 Feb;14(2):295-303. doi: 10.1517/14740338.2015.989210. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2015. PMID: 25494485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Possible Azithromycin-Induced Life-Threatening Arrhythmia Requiring Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support: A Case Report.Am J Case Rep. 2020 Nov 12;21:e926951. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.926951. Am J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33180749 Free PMC article.
-
Arrhythmia risk in liver cirrhosis.World J Hepatol. 2015 Apr 8;7(4):662-72. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i4.662. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 25866603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Azithromycin, cardiovascular risks, QTc interval prolongation, torsade de pointes, and regulatory issues: A narrative review based on the study of case reports.Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013 Oct;1(5):155-65. doi: 10.1177/2049936113501816. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 25165550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selzer A, Wray HW. Quinidine syncope. Paroxysmal ventricular fibrillation occurring during treatment of chronic atrial arrhythmias. Circulation. 1964;30:17–26. - PubMed
-
- De Bruin ML, Pettersson M, Meyboom RH, et al. Anti-HERG activity and the risk of drug-induced arrhythmias and sudden death. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:590–7. - PubMed
-
- Roden DM, Lazzara R, Rosen M, et al. Multiple mechanisms in the long-QT syndrome. Current knowledge, gaps, and future directions. The SADS Foundation Task Force on LQTS. Circulation. 1996;94:1996–2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
