AMPK as a metabolic tumor suppressor: control of metabolism and cell growth
- PMID: 20222801
- PMCID: PMC2854547
- DOI: 10.2217/fon.09.174
AMPK as a metabolic tumor suppressor: control of metabolism and cell growth
Abstract
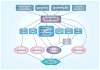
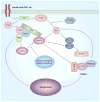
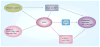
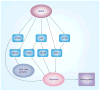
AMPK is an evolutionarily conserved fuel-sensing enzyme that is activated in shortage of energy and suppressed in its surfeit. AMPK activation stimulates fatty acid oxidation, enhances insulin sensitivity, alleviates hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia, and inhibits proinflammatory changes. Thus, AMPK is a well-received therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome and Type 2 diabetes. Recent studies indicate that AMPK plays a role in linking metabolic syndrome and cancer. AMPK is an essential mediator of the tumor suppressor LKB1 and could be suppressed in cancer cells containing loss-of-function mutations of LKB1 or containing active mutations of B-Raf, or in cancers associated with metabolic syndrome. The activation of AMPK reprograms cellular metabolism and enforces metabolic checkpoints by acting on mTORC1, p53, fatty acid synthase and other molecules for regulating cell growth and metabolism. In keeping with in vitro studies, recent epidemiological studies indicate that the incidence of cancer is reduced in Type 2 diabetes treated with metformin, an AMPK activator. Thus, AMPK is emerging as an interesting metabolic tumor suppressor and a promising target for cancer prevention and therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting AMPK for cancer prevention and treatment.Oncotarget. 2015 Apr 10;6(10):7365-78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3629. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25812084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Important role of the LKB1-AMPK pathway in suppressing tumorigenesis in PTEN-deficient mice.Biochem J. 2008 Jun 1;412(2):211-21. doi: 10.1042/BJ20080557. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18387000
-
Discovery of Pyridones As Oral AMPK Direct Activators.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013 May 17;4(7):632-6. doi: 10.1021/ml400157g. eCollection 2013 Jul 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 24900722 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin and cancer.Rev Diabet Stud. 2013 Winter;10(4):228-35. doi: 10.1900/RDS.2013.10.228. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Rev Diabet Stud. 2013. PMID: 24841876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LKB1 and AMPK maintain epithelial cell polarity under energetic stress.J Cell Biol. 2007 May 7;177(3):387-92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200702053. Epub 2007 Apr 30. J Cell Biol. 2007. Retraction in: J Cell Biol. 2013 Oct 28;203(2):373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20070205310112013r. PMID: 17470638 Free PMC article. Retracted.
Cited by
-
ATM and LKB1 dependent activation of AMPK sensitizes cancer cells to etoposide-induced apoptosis.Cancer Lett. 2013 Jan 1;328(1):114-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.08.034. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 22960274 Free PMC article.
-
The proline regulatory axis and cancer.Front Oncol. 2012 Jun 21;2:60. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2012.00060. eCollection 2012. Front Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22737668 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer cell signaling pathways targeted by spice-derived nutraceuticals.Nutr Cancer. 2012;64(2):173-97. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2012.630551. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Nutr Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22149093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy Restriction and Colorectal Cancer: A Call for Additional Research.Nutrients. 2020 Jan 1;12(1):114. doi: 10.3390/nu12010114. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 31906264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPK targets a proto-oncogene TPD52 (isoform 3) expression and its interaction with LKB1 suppress AMPK-GSK3β signaling axis in prostate cancer.J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):957-974. doi: 10.1007/s12079-023-00745-y. Epub 2023 Apr 11. J Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37040029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steinberg GR, Kemp BE. AMPK in health and Disease. Physiol Rev. 2009;89(3):1025–1078. - PubMed
-
- Ruderman N, Prentki M. AMP kinase and malonyl-CoA: targets for therapy of the metabolic syndrome. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3(4):340–351. - PubMed
-
- Luo Z, Saha AK, Xiang X, Ruderman NB. AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26(2):69–76. - PubMed
-
- Hoyer-Hansen M, Jaattela M. AMP-activated protein kinase: a universal regulator of autophagy? Autophagy. 2007;3(4):381–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
