Depletion of the non-coding regulatory 6S RNA in E. coli causes a surprising reduction in the expression of the translation machinery
- PMID: 20222947
- PMCID: PMC2848244
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-165
Depletion of the non-coding regulatory 6S RNA in E. coli causes a surprising reduction in the expression of the translation machinery
Abstract
Background: 6S RNA from E. coli is known to bind to RNA polymerase interfering with transcription initiation. Because 6S RNA concentrations are maximal at stationary phase and binding occurs preferentially to the holoenzyme associated with sigma(70) (Esigma(70)) it is believed that 6S RNA supports adjustment to stationary phase transcription. Previous studies have also suggested that inhibition is specific for sigma(70)-dependent promoters characterized by a weak -35 recognition motif or extended -10 promoters. There are many exceptions to this precept, showing that other types of promoters, including stationary phase-specific (sigma(38)-dependent) promoters are inhibited.
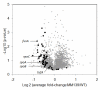
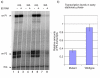
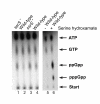
Results: To solve this apparent ambiguity and to better understand the role of 6S RNA in stationary phase transition we have performed a genome-wide transcriptional analysis of wild-type and 6S RNA deficient cells growing to mid-log or early stationary phase. We found 245 genes at the exponential growth phase and 273 genes at the early stationary phase to be > or = 1.5-fold differentially expressed. Up- and down-regulated genes include many transcriptional regulators, stress-related proteins, transporters and several enzymes involved in purine metabolism. As the most striking result during stationary phase, however, we obtained in the 6S RNA deficient strain a concerted expression reduction of genes constituting the translational apparatus. In accordance, primer extension analysis showed that transcription of ribosomal RNAs, representing the key molecules for ribosome biogenesis, is also significantly reduced under the same conditions. Consistent with this finding biochemical analysis of the 6S RNA deficient strain indicates that the lack of 6S RNA is apparently compensated by an increase of the basal ppGpp concentration, known to affect growth adaptation and ribosome biogenesis.
Conclusions: The analysis demonstrated that the effect of 6S RNA on transcription is not strictly confined to sigma(70)-dependent promoters. Moreover, the results indicate that 6S RNA is embedded in stationary phase adaptation, which is governed by the capacity of the translational machinery.
Figures


References
-
- Gildehaus N, Neusser T, Wurm R, Wagner R. Studies on the function of the riboregulator 6S RNA from E. coli: RNA polymerase binding, inhibition of in vitro transcription and synthesis of RNA-directed de novo transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(6):1885–1896. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm085. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

