A meta-analysis of genome-wide data from five European isolates reveals an association of COL22A1, SYT1, and GABRR2 with serum creatinine level
- PMID: 20222955
- PMCID: PMC2848223
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-41
A meta-analysis of genome-wide data from five European isolates reveals an association of COL22A1, SYT1, and GABRR2 with serum creatinine level
Abstract
Background: Serum creatinine (S CR) is the most important biomarker for a quick and non-invasive assessment of kidney function in population-based surveys. A substantial proportion of the inter-individual variability in S CR level is explicable by genetic factors.
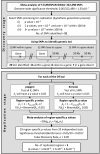
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of S CR undertaken in five population isolates ('discovery cohorts'), all of which are part of the European Special Population Network (EUROSPAN) project. Genes showing the strongest evidence for an association with SCR (candidate loci) were replicated in two additional population-based samples ('replication cohorts').
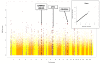
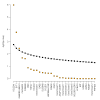
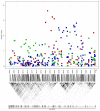
Results: After the discovery meta-analysis, 29 loci were selected for replication. Association between SCR level and polymorphisms in the collagen type XXII alpha 1 (COL22A1) gene, on chromosome 8, and in the synaptotagmin-1 (SYT1) gene, on chromosome 12, were successfully replicated in the replication cohorts (p value = 1.0 x 10(-6) and 1.7 x 10(-4), respectively). Evidence of association was also found for polymorphisms in a locus including the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor rho-2 (GABRR2) gene and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2-J1 (UBE2J1) gene (replication p value = 3.6 x 10(-3)). Previously reported findings, associating glomerular filtration rate with SNPs in the uromodulin (UMOD) gene and in the schroom family member 3 (SCHROOM3) gene were also replicated.
Conclusions: While confirming earlier results, our study provides new insights in the understanding of the genetic basis of serum creatinine regulatory processes. In particular, the association with the genes SYT1 and GABRR2 corroborate previous findings that highlighted a possible role of the neurotransmitters GABAA receptors in the regulation of the glomerular basement membrane and a possible interaction between GABAA receptors and synaptotagmin-I at the podocyte level.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A genome-wide association study identifies five loci influencing facial morphology in Europeans.PLoS Genet. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002932. Epub 2012 Sep 13. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23028347 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Association Study of Renal Function Traits: Results from the Japan Multi-Institutional Collaborative Cohort Study.Am J Nephrol. 2018;47(5):304-316. doi: 10.1159/000488946. Epub 2018 May 18. Am J Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29779033
-
Identification of a New Susceptibility Locus for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus on Chromosome 12 in Individuals of European Ancestry.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;68(1):174-83. doi: 10.1002/art.39403. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26316170 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide linkage analysis of serum creatinine in three isolated European populations.Kidney Int. 2009 Aug;76(3):297-306. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.135. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Kidney Int. 2009. PMID: 19387472
-
Four novel Loci (19q13, 6q24, 12q24, and 5q14) influence the microcirculation in vivo.PLoS Genet. 2010 Oct 28;6(10):e1001184. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001184. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 21060863 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic susceptibility to hypertensive renal disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Nov;69(22):3751-63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0996-3. Epub 2012 May 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22562581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive value of 8 genetic loci for serum uric acid concentration.Croat Med J. 2010 Feb;51(1):23-31. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2010.51.23. Croat Med J. 2010. PMID: 20162742 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Alström syndrome 1 in the regulation of blood pressure and renal function.JCI Insight. 2018 Nov 2;3(21):e95076. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.95076. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30385718 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on GABAρ Receptors.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010 Dec;8(4):422-33. doi: 10.2174/157015910793358141. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2010. PMID: 21629448 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic association in female stress urinary incontinence based on proteomic findings: a case-control study.Int Urogynecol J. 2020 Jan;31(1):117-122. doi: 10.1007/s00192-019-03878-0. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Int Urogynecol J. 2020. PMID: 30715578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whitfield JB, Martin NG. The effects of inheritance on constituents of plasma: a twin study on some biochemical variables. Ann Clin Biochem. 1984;21(3):176–183. - PubMed
-
- Pattaro C, Aulchenko YS, Isaacs A, Vitart V, Hayward C, Franklin CS, Polasek O, Kolcic I, Biloglav Z, Campbell S, Hastie N, Lauc G, Meitinger T, Oostra BA, Gyllensten U, Wilson JF, Pichler I, Hicks AA, Campbell H, Wright AF, Rudan I, van Duijn CM, Riegler P, Marroni F, Pramstaller PP. Genome-wide linkage analysis of serum creatinine in three isolated European populations. Kidney Int. 2009;76(3):297–306. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.135. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fox CS, Yang Q, Cupples LA, Guo CY, Larson MG, Leip EP, Wilson PW, Levy D. Genomewide linkage analysis to serum creatinine, GFR, and creatinine clearance in a community-based population: the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(9):2457–2461. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000135972.13396.6F. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

