The first set of EST resource for gene discovery and marker development in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.)
- PMID: 20222972
- PMCID: PMC2923520
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-45
The first set of EST resource for gene discovery and marker development in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan L.)
Abstract
Background: Pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp) is one of the major grain legume crops of the tropics and subtropics, but biotic stresses [Fusarium wilt (FW), sterility mosaic disease (SMD), etc.] are serious challenges for sustainable crop production. Modern genomic tools such as molecular markers and candidate genes associated with resistance to these stresses offer the possibility of facilitating pigeonpea breeding for improving biotic stress resistance. Availability of limited genomic resources, however, is a serious bottleneck to undertake molecular breeding in pigeonpea to develop superior genotypes with enhanced resistance to above mentioned biotic stresses. With an objective of enhancing genomic resources in pigeonpea, this study reports generation and analysis of comprehensive resource of FW- and SMD- responsive expressed sequence tags (ESTs).
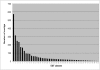
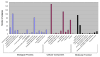
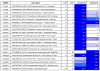
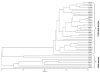
Results: A total of 16 cDNA libraries were constructed from four pigeonpea genotypes that are resistant and susceptible to FW ('ICPL 20102' and 'ICP 2376') and SMD ('ICP 7035' and 'TTB 7') and a total of 9,888 (9,468 high quality) ESTs were generated and deposited in dbEST of GenBank under accession numbers GR463974 to GR473857 and GR958228 to GR958231. Clustering and assembly analyses of these ESTs resulted into 4,557 unique sequences (unigenes) including 697 contigs and 3,860 singletons. BLASTN analysis of 4,557 unigenes showed a significant identity with ESTs of different legumes (23.2-60.3%), rice (28.3%), Arabidopsis (33.7%) and poplar (35.4%). As expected, pigeonpea ESTs are more closely related to soybean (60.3%) and cowpea ESTs (43.6%) than other plant ESTs. Similarly, BLASTX similarity results showed that only 1,603 (35.1%) out of 4,557 total unigenes correspond to known proteins in the UniProt database (<or= 1E-08). Functional categorization of the annotated unigenes sequences showed that 153 (3.3%) genes were assigned to cellular component category, 132 (2.8%) to biological process, and 132 (2.8%) in molecular function. Further, 19 genes were identified differentially expressed between FW- responsive genotypes and 20 between SMD- responsive genotypes. Generated ESTs were compiled together with 908 ESTs available in public domain, at the time of analysis, and a set of 5,085 unigenes were defined that were used for identification of molecular markers in pigeonpea. For instance, 3,583 simple sequence repeat (SSR) motifs were identified in 1,365 unigenes and 383 primer pairs were designed. Assessment of a set of 84 primer pairs on 40 elite pigeonpea lines showed polymorphism with 15 (28.8%) markers with an average of four alleles per marker and an average polymorphic information content (PIC) value of 0.40. Similarly, in silico mining of 133 contigs with >or= 5 sequences detected 102 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 37 contigs. As an example, a set of 10 contigs were used for confirming in silico predicted SNPs in a set of four genotypes using wet lab experiments. Occurrence of SNPs were confirmed for all the 6 contigs for which scorable and sequenceable amplicons were generated. PCR amplicons were not obtained in case of 4 contigs. Recognition sites for restriction enzymes were identified for 102 SNPs in 37 contigs that indicates possibility of assaying SNPs in 37 genes using cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) assay.
Conclusion: The pigeonpea EST dataset generated here provides a transcriptomic resource for gene discovery and development of functional markers associated with biotic stress resistance. Sequence analyses of this dataset have showed conservation of a considerable number of pigeonpea transcripts across legume and model plant species analysed as well as some putative pigeonpea specific genes. Validation of identified biotic stress responsive genes should provide candidate genes for allele mining as well as candidate markers for molecular breeding.
Figures







References
-
- Varshney RK, Hoisington DA, Upadhyaya HD, Gaur PM, Nigam SN, Saxena KB, Vadez V, Sethy NK, Bhatia S, Aruna R, Channabyre Gowda MV, Singh NK. In: Genomic-Assisted crop improvement. Varshney RK, Tuberosa R, editor. Springer Netherlands, The Netherlands; 2007. Molecular genetics and breeding of grain legume crops for the semi-arid tropics; pp. 207–241. full_text.
-
- Greilhuber J, Obermayer R. Genome size variation in Cajanus cajan (Fabaceae): a reconsideration. Plant Syst Evol. 1998;212:135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00985225. - DOI
-
- FAOSTAT 2006. http://faostat.fao.org
-
- Rao SC, Coleman SW, Mayeux HS. Forage production and nutritive value of selected pigeonpea ecotypes in the southern great plains. Crop Sci. 2002;42:1259–1263.
-
- Prasad P, Eswara Reddy NP, Anandam RJ, Lakshmikantha Reddy G. Isozymes variability among Fusarium udum resistant cultivars of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) (Millsp) Acta Physiol Plant. 2003;25:221–228. doi: 10.1007/s11738-003-0001-8. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

