Gene expression profiling of xeroderma pigmentosum
- PMID: 20223010
- PMCID: PMC2837287
- DOI: 10.1186/1897-4287-4-2-103
Gene expression profiling of xeroderma pigmentosum
Abstract
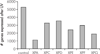
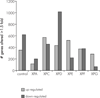
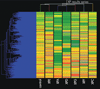
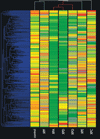
Xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) is a rare recessive disorder that is characterized by extreme sensitivity to UV light. UV light exposure results in the formation of DNA damage such as cyclobutane dimers and (6-4) photoproducts. Nucleotide excision repair (NER) orchestrates the removal of cyclobutane dimers and (6-4) photoproducts as well as some forms of bulky chemical DNA adducts. The disease XP is comprised of 7 complementation groups (XP-A to XP-G), which represent functional deficiencies in seven different genes, all of which are believed to be involved in NER. The main clinical feature of XP is various forms of skin cancers; however, neurological degeneration is present in XPA, XPB, XPD and XPG complementation groups. The relationship between NER and other types of DNA repair processes is now becoming evident but the exact relationships between the different complementation groups remains to be precisely determined.Using gene expression analysis we have identified similarities and differences after UV light exposure between the complementation groups XP-A, XP-C, XP-D, XP-E, XP-F, XP-G and an unaffected control. The results reveal that there is a graded change in gene expression patterns between the mildest, most similar to the control response (XP-E) and the severest form (XP-A) of the disease, with the exception of XP-D. Distinct differences between the complementation groups with neurological symptoms (XP-A, XP-D and XP-G) and without (XP-C, XP-E and XP-F) were also identified. Therefore, this analysis has revealed distinct gene expression profiles for the XP complementation groups and the first step towards understanding the neurological symptoms of XP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding Xeroderma Pigmentosum Complementation Groups Using Gene Expression Profiling after UV-Light Exposure.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jul 14;16(7):15985-96. doi: 10.3390/ijms160715985. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26184184 Free PMC article.
-
Sunlight, Vitamin D, and Xeroderma Pigmentosum.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1268:319-331. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-46227-7_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32918226 Review.
-
Comparative study of nucleotide excision repair defects between XPD-mutated fibroblasts derived from trichothiodystrophy and xeroderma pigmentosum patients.DNA Repair (Amst). 2008 Dec 1;7(12):1990-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.08.009. Epub 2008 Oct 10. DNA Repair (Amst). 2008. PMID: 18817897
-
Xeroderma pigmentosum and molecular cloning of DNA repair genes.Anticancer Res. 1996 Mar-Apr;16(2):693-708. Anticancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8687116 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of xeroderma pigmentosum (XP) proteins.Q Rev Biophys. 2016 Jan;49:e5. doi: 10.1017/S0033583515000268. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Q Rev Biophys. 2016. PMID: 27660069
Cited by
-
Understanding Xeroderma Pigmentosum Complementation Groups Using Gene Expression Profiling after UV-Light Exposure.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jul 14;16(7):15985-96. doi: 10.3390/ijms160715985. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26184184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer M, Berg P. Genes and genomes: a changing perspective. USA: University Science Press; 1991.
-
- Klug WS, Cummings MR. Concepts in Genetics. USA: Macmillan College Publishing Company Inc; 1994.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
