Von hippel-lindau disease
- PMID: 20223044
- PMCID: PMC2837060
- DOI: 10.1186/1897-4287-3-4-171
Von hippel-lindau disease
Abstract
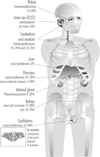
A germline mutation in the Von-Hippel Lindau (VHL) gene predisposes carriers to development of abundantly vascularised tumours in the retina, cerebellum, spine, kidney, adrenal gland and pancreas. Most VHL patients die from the consequences of cerebellar haemangioblastoma or renal cell carcinoma. The VHL gene is a tumour suppressor gene and is involved in angiogenesis by regulation of the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1-alpha). Clinical diagnosis of VHL can be confirmed by molecular genetic analysis of the VHL gene, which is informative in virtually all VHL families. A patient with (suspicion for) VHL is an indication for genetic counselling and periodical examination.
Figures

References
-
- Hes F. Von Hippel-Lindau disease: clinical and genetic investigations in the Netherlands. Utrecht University, thesis; 2000.
-
- Richard S, Campello C, Taillandier L, Parker F, Resche F. Haemangioblastoma of the central nervous system in von Hippel-Lindau disease. French VHL Study Group. J Intern Med. 1998;243(6):547–553. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
