Neonatal Escherichia coli infection alters glial, cytokine, and neuronal gene expression in response to acute amphetamine in adolescent rats
- PMID: 20223277
- PMCID: PMC2865898
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.03.006
Neonatal Escherichia coli infection alters glial, cytokine, and neuronal gene expression in response to acute amphetamine in adolescent rats
Abstract
Neonatal bacterial infection in rats alters the responses to a variety of subsequent challenges later in life. Here we explored the effects of neonatal bacterial infection on a subsequent drug challenge during adolescence, using administration of the psychostimulant amphetamine. Male rat pups were injected on postnatal day 4 (P4) with live Escherichia coli (E. coli) or PBS vehicle, and then received amphetamine (15mg/kg) or saline on P40. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed on micropunches taken from medial prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and the CA1 subfield of the hippocampus. mRNA for glial and neuronal activation markers as well as pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines were assessed. Amphetamine produced brain region specific increases in many of these genes in PBS controls, while these effects were blunted or absent in neonatal E. coli treated rats. In contrast to the potentiating effect of neonatal E. coli on glial and cytokine responses to an immune challenge previously observed, neonatal E. coli infection attenuates glial and cytokine responses to an amphetamine challenge.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
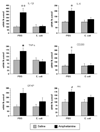
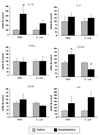
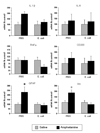
Similar articles
-
Effect of melatonin on D-amphetamine-induced neuroglial alterations in postnatal rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex.Neurosci Lett. 2012 Aug 22;524(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.06.077. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Neurosci Lett. 2012. PMID: 22796652
-
Neonatal ventral hippocampus lesion leads to reductions in nerve growth factor inducible-B mRNA in the prefrontal cortex and increased amphetamine response in the nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum.Neuroscience. 2003;122(3):669-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.08.016. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 14622910
-
Heat shock protein 27 shows a distinctive widespread spatial and temporal pattern of induction in CNS glial and neuronal cells compared to heat shock protein 70 and caspase 3 following kainate administration.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001 Sep 30;93(2):148-63. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(01)00199-1. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11589992
-
[Experimental study on cerebral white matter damage in neonatal rat after intrauterine Escherichia coli infection].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2003 Dec;41(12):893-6. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14723807 Chinese.
-
White matter damage and chemokine induction in developing rat brain after intrauterine infection.J Perinat Med. 2005;33(5):415-22. doi: 10.1515/JPM.2005.074. J Perinat Med. 2005. PMID: 16238536
Cited by
-
Microglial Function in the Effects of Early-Life Stress on Brain and Behavioral Development.J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 8;9(2):468. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020468. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 32046333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic stress enhances microglia activation and exacerbates death of nigral dopaminergic neurons under conditions of inflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Feb 24;11:34. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-34. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24565378 Free PMC article.
-
The immune system and developmental programming of brain and behavior.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Aug;33(3):267-86. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Sep 9. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22982535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microglia and memory: modulation by early-life infection.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 26;31(43):15511-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3688-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22031897 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay of early-life stress, nutrition, and immune activation programs adult hippocampal structure and function.Front Mol Neurosci. 2015 Jan 9;7:103. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00103. eCollection 2014. Front Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25620909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baicy K, London ED. Corticolimbic dysregulation and chronic methamphetamine abuse. Addiction. 2007;102 Suppl 1:5–15. - PubMed
-
- Bilbo SD, Barrientos RM, Eads AS, Northcutt A, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Early-life infection leads to altered BDNF and IL-1beta mRNA expression in rat hippocampus following learning in adulthood. Brain Behav Immun. 2008;22:451–455. - PubMed
-
- Bilbo SD, Levkoff LH, Mahoney JH, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Neonatal infection induces memory impairments following an immune challenge in adulthood. Behav Neurosci. 2005;119:293–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

