Trends in inpatient prolapse procedures in the United States, 1979-2006
- PMID: 20223444
- PMCID: PMC3097054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.01.017
Trends in inpatient prolapse procedures in the United States, 1979-2006
Abstract
Objective: We sought to describe national trends for inpatient procedures for pelvic organ prolapse from 1979-2006.
Study design: The National Hospital Discharge Survey was analyzed for patient and hospital demographics, as were International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification diagnostic and procedures codes from 1979-2006. Age-adjusted rates (AARs) per 1000 women were calculated using the 1990 US Census data.
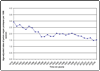
Results: There was a significantly decreasing trend in the AARs for inpatient prolapse procedures, from 2.93-1.52 per 1000 women from 1979-2006. AARs for hysterectomy decreased from 8.39-4.55 per 1000 women from 1979-2006. Over the study period, AARs remained at about the 1979 level among the women>or=52 years old (2.73-2.86; P=.075). In women<52 years old, AARs declined to less than one-third of the 1979 rate (3.03-0.84; P<.001).
Conclusion: AARs for inpatient procedures for prolapse in the United States remained stable for women aged>or=52 years from 1979-2006; rates declined by two-thirds for women aged<52 years.
Copyright (c) 2010 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Delancey JO. The hidden epidemic of pelvic floor dysfunction: Achievable goals for improved prevention and treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2005;192:1488–1495. - PubMed
-
- Olsen Al, Smith VJ, Bergstrom JO, Colling JC, Clark AL. Epidemiology of surgically managed pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 1991;89:501–506. - PubMed
-
- Boyles SH, Weber AM, Meyn L. Procedures for pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence in the United States, 1979–1997. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;188:108–115. - PubMed
-
- Subak LL, Waetjen E, van den Eeden S, Thom DH, Vittinghoff E, Brown JS. Cost of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Surgery in the United States. Obstet Gynecol. 2001;98:646–651. - PubMed
-
- Swift SE. The distribution of pelvic organ support in a population of subjects seen for routine gynecologic care. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000;183:277–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous