Sensor domains of two-component regulatory systems
- PMID: 20223701
- PMCID: PMC3078554
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.01.016
Sensor domains of two-component regulatory systems
Abstract
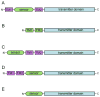
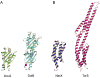
Two-component systems regulate crucial cellular processes in microorganisms, and each comprises a homodimeric histidine kinase receptor and a cytoplasmic response regulator. Histidine kinases, often membrane associated, detect environmental input at sensor domains and propagate resulting signals to catalytic cytoplasmic transmitter domains. Recent studies on the great diversity of sensor domains reveal patterns of domain organization and biochemical properties that provide insight into mechanisms of signaling. Despite the enormous sequence variability found within sensor input domains, they fall into a relatively small number of discrete structural classes. Subtle rearrangements along a structurally labile dimer interface, in the form of possible sliding or rotational motions, are propagated from the sensor domain to the transmitter domain to modulate activity of the receptor.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
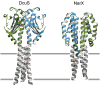
References
-
- Dutta R, Qin L, Inouye M. Histidine kinases: diversity of domain organization. Mol Microbiol. 1999;34:633–640. - PubMed
-
- Kirby JR. Chemotaxis-Like Regulatory Systems: Unique Roles in Diverse Bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2009;63:45–59. - PubMed
-
- Cheung J, Bingman CA, Reyngold M, Hendrickson WA, Waldburger CD. Crystal structure of a functional dimer of the PhoQ sensor domain. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:13762–13770. The structure of a biologically relevant PDC sensor domain dimer is characterized for the first time with supporting in vivo data. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cho US, Bader MW, Amaya MF, Daley ME, Klevit RE, Miller SI, Xu WQ. Metal bridges between the PhoQ sensor domain and the membrane regulate transmembrane signaling. J Mol Biol. 2006;356:1193–1206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

