Flightless-I (Fli-I) regulates the actin assembly activity of diaphanous-related formins (DRFs) Daam1 and mDia1 in cooperation with active Rho GTPase
- PMID: 20223827
- PMCID: PMC2871490
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.079236
Flightless-I (Fli-I) regulates the actin assembly activity of diaphanous-related formins (DRFs) Daam1 and mDia1 in cooperation with active Rho GTPase
Abstract
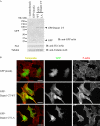
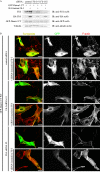
Eukaryotic cells dynamically reorganize the actin cytoskeleton to regulate various cellular activities, such as cell shape change, cell motility, cytokinesis, and vesicular transport. Diaphanous-related formins (DRFs), such as Daam1 and mDia1, play central roles in actin dynamics through assembling linear actin filaments. It has been reported that the GTP-bound active Rho binds directly to DRFs and partially unleashes the intramolecular autoinhibition of DRFs. However, whether proteins other than Rho involve the regulation of the actin assembly activity of DRFs has been unclear. Here, we show that Flightless-I (Fli-I), a gelsolin family protein essential for early development, binds directly to Daam1 and mDia1. Fli-I enhances the intrinsic actin assembly activity of Daam1 and mDia1 in vitro and is required for Daam1-induced actin assembly in living cells. Furthermore, Fli-I promotes the GTP-bound active Rho-mediated relief of the autoinhibition of Daam1 and mDia1. Thus, Fli-I is a novel positive regulator of Rho-induced linear actin assembly mediated by DRFs.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Biochemical characterization of the Rho GTPase-regulated actin assembly by diaphanous-related formins, mDia1 and Daam1, in platelets.J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 28;283(13):8746-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707839200. Epub 2008 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18218625
-
Structure of the FH2 domain of Daam1: implications for formin regulation of actin assembly.J Mol Biol. 2007 Jun 22;369(5):1258-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.002. Epub 2007 Apr 5. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17482208 Free PMC article.
-
Formins as effector proteins of Rho GTPases.Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29513. doi: 10.4161/sgtp.29513. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 24914801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diaphanous-related formin DAAM1 collaborates with the Rho GTPases RhoA and Cdc42, CIP4 and Src in regulating cell morphogenesis and actin dynamics.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Jul 15;312(12):2180-94. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.03.013. Epub 2006 Apr 21. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16630611
-
Mechanism and function of formins in the control of actin assembly.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:593-627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142647. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17373907 Review.
Cited by
-
Multifunctional Roles of the Actin-Binding Protein Flightless I in Inflammation, Cancer and Wound Healing.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 24;8:603508. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.603508. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33330501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The scaffold-protein IQGAP1 enhances and spatially restricts the actin-nucleating activity of Diaphanous-related formin 1 (DIAPH1).J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):3134-3147. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010476. Epub 2020 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32005666 Free PMC article.
-
Flightless I interacts with NMMIIA to promote cell extension formation, which enables collagen remodeling.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Jun 15;26(12):2279-97. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-11-1536. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25877872 Free PMC article.
-
SPIN90 associates with mDia1 and the Arp2/3 complex to regulate cortical actin organization.Nat Cell Biol. 2020 Jul;22(7):803-814. doi: 10.1038/s41556-020-0531-y. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Nat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32572169
-
There is more than one way to model an elephant. Experiment-driven modeling of the actin cytoskeleton.Biophys J. 2013 Feb 5;104(3):520-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.12.044. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23442903 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Faix J., Grosse R. (2006) Dev. Cell 10, 693–706 - PubMed
-
- Higgs H. N. (2005) Trends Biochem. Sci. 30, 342–353 - PubMed
-
- Pruyne D., Evangelista M., Yang C., Bi E., Zigmond S., Bretscher A., Boone C. (2002) Science 297, 612–615 - PubMed
-
- Sagot I., Rodal A. A., Moseley J., Goode B. L., Pellman D. (2002) Nat. Cell Biol. 4, 626–631 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

