Disruption of SM22 promotes inflammation after artery injury via nuclear factor kappaB activation
- PMID: 20224039
- PMCID: PMC2896867
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.213900
Disruption of SM22 promotes inflammation after artery injury via nuclear factor kappaB activation
Abstract
Rationale: SM22 (or transgelin), an actin-binding protein abundant in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), is downregulated in atherosclerosis, aneurysm and various cancers. Abolishing SM22 in apolipoprotein E knockout mice accelerates atherogenesis. However, it is unclear whether SM22 disruption independently promotes arterial inflammation.
Objective: To investigate whether SM22 disruption directly promotes inflammation on arterial injury and to characterize the underlying mechanisms.
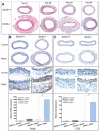
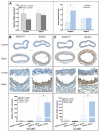
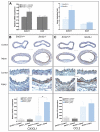
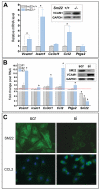
Methods and results: Using carotid denudation as an artery injury model, we showed that Sm22 knockout (Sm22(-/-)) mice developed enhanced inflammatory responses with higher induction of proinflammatory genes, including Vcam1, Icam1, Cx3cl1, Ccl2, and Ptgs2. Higher expression of these genes was confirmed in primary Sm22(-/-) VSMCs and in PAC1 cells after Sm22 knockdown, whereas SM22 recapitulation in primary Sm22(-/-) VSMCs decreased their expression. NFKB2 was prominently activated in both injured carotids of Sm22(-/-) mice and in PAC1 cells after Sm22 knockdown and may mediate upregulation of these proinflammatory genes. As a NF-kappaB activator, reactive oxygen species (ROS) increased in primary Sm22(-/-) VSMCs and in PAC1 cells after Sm22 knockdown. ROS scavengers blocked NF-kappaB activation and induction of proinflammatory genes. Furthermore, Sm22 knockdown increased Sod2 expression and activated p47phox, reflecting contributions of mitochondria and NADPH oxidase to the augmented ROS production; this may result from actin and microtubule cytoskeletal remodeling.
Conclusions: Our findings show that SM22 downregulation can induce proinflammatory VSMCs through activation of ROS-mediated NF-kappaB pathways. This study provides initial evidence linking VSMC cytoskeleton remodeling with arterial inflammation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Arterial injury promotes medial chondrogenesis in Sm22 knockout mice.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Apr 1;90(1):28-37. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq378. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21183509 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of smooth muscle 22α facilitates angiotensin II-induced ROS production via activation of the PKCδ-P47phox axis through release of PKCδ and actin dynamics and is associated with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro and in vivo.Circ Res. 2012 Aug 31;111(6):697-707. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.272013. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22798525
-
NADPH oxidase 4 regulates vascular inflammation in aging and atherosclerosis.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Jan;102:10-21. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.12.004. Epub 2016 Dec 14. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27986445 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of the Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway is involved in smooth muscle 22 alpha-mediated suppression of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointima hyperplasia.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010 Apr;30(4):683-91. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.200501. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20139360
-
[The role of SM22 alpha in cytoskeleton organization and vascular remodeling].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2006 Jul;37(3):211-5. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2006. PMID: 17009727 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Quercetin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cell Damage and Inflammation via Regulation of the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in Bovine Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Oct 27;44(11):5234-5246. doi: 10.3390/cimb44110356. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36354668 Free PMC article.
-
Smooth muscle 22 alpha protein inhibits VSMC foam cell formation by supporting normal LXRα signaling, ameliorating atherosclerosis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 22;12(11):982. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04239-w. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34686657 Free PMC article.
-
Drebrin regulates angiotensin II-induced aortic remodelling.Cardiovasc Res. 2018 Nov 1;114(13):1806-1815. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy151. Cardiovasc Res. 2018. PMID: 29931051 Free PMC article.
-
SXBX pill suppresses homocysteine-induced vascular smooth muscle cells dedifferentiation by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasomes activation via ERK/p38 MAPK pathways.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Feb 15;11(2):806-818. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 30899381 Free PMC article.
-
Decreasing mitochondrial fission diminishes vascular smooth muscle cell migration and ameliorates intimal hyperplasia.Cardiovasc Res. 2015 May 1;106(2):272-83. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvv005. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2015. PMID: 25587046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu Y, Liu HW, Forsythe SM, Kogut P, McConville JF, Halayko AJ, Camoretti-Mercado B, Solway J. Mutagenesis analysis of human SM22: characterization of actin binding. J Appl Physiol. 2000;89:1985–1990. - PubMed
-
- Assinder SJ, Stanton JA, Prasad PD. Transgelin: an actin-binding protein and tumour suppressor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009;41:482–486. - PubMed
-
- Wamhoff BR, Hoofnagle MH, Burns A, Sinha S, McDonald OG, Owens GK. A G/C element mediates repression of the SM22alpha promoter within phenotypically modulated smooth muscle cells in experimental atherosclerosis. Circulation research. 2004;95:981–988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

