Matrix-specific protein kinase A signaling regulates p21-activated kinase activation by flow in endothelial cells
- PMID: 20224042
- PMCID: PMC2862370
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.210286
Matrix-specific protein kinase A signaling regulates p21-activated kinase activation by flow in endothelial cells
Abstract
Rationale: Atherosclerosis is initiated by blood flow patterns that activate inflammatory pathways in endothelial cells. Activation of inflammatory signaling by fluid shear stress is highly dependent on the composition of the subendothelial extracellular matrix. The basement membrane proteins laminin and collagen found in normal vessels suppress flow-induced p21 activated kinase (PAK) and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation. By contrast, the provisional matrix proteins fibronectin and fibrinogen found in wounded or inflamed vessels support flow-induced PAK and NF-kappaB activation. PAK mediates both flow-induced permeability and matrix-specific activation of NF-kappaB.
Objective: To elucidate the mechanisms regulating matrix-specific PAK activation.
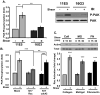
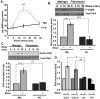
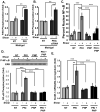
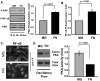
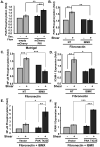
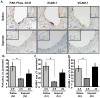
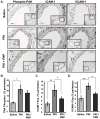
Methods and results: We now show that matrix composition does not affect the upstream pathway by which flow activates PAK (integrin activation, Rac). Instead, basement membrane proteins enhance flow-induced protein kinase (PK)A activation, which suppresses PAK. Inhibiting PKA restored flow-induced PAK and NF-kappaB activation in cells on basement membrane proteins, whereas stimulating PKA inhibited flow-induced activation of inflammatory signaling in cells on fibronectin. PKA suppressed inflammatory signaling through PAK inhibition. Activating PKA by injection of the prostacyclin analog iloprost reduced PAK activation and inflammatory gene expression at sites of disturbed flow in vivo, whereas inhibiting PKA by PKA inhibitor (PKI) injection enhanced PAK activation and inflammatory gene expression. Inhibiting PAK prevented the enhancement of inflammatory gene expression by PKI.
Conclusions: Basement membrane proteins inhibit inflammatory signaling in endothelial cells via PKA-dependent inhibition of PAK.
Figures
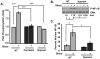
References
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 1999;340:115–126. [see comment] - PubMed
-
- Gimbrone MA, Jr, Topper JN, Nagel T, Anderson KR, Garcia-Cardena G. Endothelial dysfunction, hemodynamic forces, and atherogenesis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2000;902:230–239. discussion 239–240. - PubMed
-
- Mohan S, Mohan N, Sprague EA. Differential activation of NF-kappa B in human aortic endothelial cells conditioned to specific flow environments. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:C572–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

