Population attributable fractions for late postnatal mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Sub-Saharan Africa
- PMID: 20224418
- PMCID: PMC3086731
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181d61c2e
Population attributable fractions for late postnatal mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Sub-Saharan Africa
Abstract
Objectives: Assess population attributable fractions (PAFs) for late postnatal transmission (LPT) of HIV-1 in a cohort of HIV-1-exposed infants.
Methods: We used data established from a risk factor analysis of LPT (negative HIV-1 results through the 4-6 week visit, but positive assays thereafter through the 12-month visit) from a perinatal clinical trial conducted in 3 sub-Saharan countries. PAFs were calculated as the proportions of excess LPTs attributed to identified risk factors.
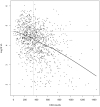
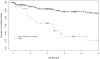
Results: For the cohort of 1317 infants, 206 (15.6%) had only low maternal CD4 counts (<200 cells/mm), 332 (25.2%) had only high maternal plasma viral loads (VLs) (>50,000 copies/mL), and 81 (6.2%) had both low CD4 counts and high VLs. Their PAFs were 26.0% [95% confidence interval (CI): 12.0% to 36.0%], 37.0% (95% CI: 22.0% to 51.0%), and 16.0% (95% CI: 6.0% to 25.0%), respectively.
Conclusions: Our PAF analysis illustrates the public health impact of the substantial proportion of LPTs accounted for by high-risk women with both low CD4 counts and high VLs. In light of these results, access to and use of antiretroviral therapy by high-risk HIV-1-infected pregnant women is essential. Additional strategies to reduce LPT for those not meeting criteria for antiretroviral therapy should be implemented.
Figures
References
-
- The Working Group on Mother-to-Child Transmission of HIV Rates of mother-to-child transmission of HIV-1 in Africa, America, and Europe: results from 13 perinatal studies. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995;8:506–510. - PubMed
-
- The Breastfeeding and HIV International Transmission Study (BHITS) Group Late postnatal transmission of HIV-1 in breastfed children: an individual patient data metaanalysis. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:2154–2166. - PubMed
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) UNAIDS; Geneva, Switzerland: 2008. Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic, Ch. 2. Available at: http://data.unaids.org/pub/GlobalReport/2008/jc1510_2008_global_report_p....
-
- Mason E. Positioning paediatric HIV in the child survival agenda: presentation to UNICEF-WHO consultation. UNICEF; New York: Jan 11-13, 2006. 2006. Available at http://data.unaids.org/pub/GlobalReport/2008/jc1510_2008_global_report_p....
-
- Taha TE, Kumwenda NI, Hoover DR, et al. Association of HIV-1 load and CD4 lymphocyte count with mortality among untreated African children over one year of age. AIDS. 2000;14:453–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials