Identification of diagnostic urinary biomarkers for acute kidney injury
- PMID: 20224435
- PMCID: PMC2864920
- DOI: 10.231/JIM.0b013e3181d473e7
Identification of diagnostic urinary biomarkers for acute kidney injury
Abstract
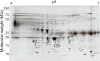
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is an important cause of death among hospitalized patients. The 2 most common causes of AKI are acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and prerenal azotemia (PRA). Appropriate diagnosis of the disease is important but often difficult. We analyzed urine proteins by 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis from 38 patients with AKI. Patients were randomly assigned to a training set, an internal test set, or an external validation set. Spot abundances were analyzed by artificial neural networks to identify biomarkers that differentiate between ATN and PRA. When the trained neural network algorithm was tested against the training data, it identified the diagnosis for 16 of 18 patients in the training set and all 10 patients in the internal test set. The accuracy was validated in the novel external set of patients where conditions of 9 of 10 patients were correctly diagnosed including 5 of 5 with ATN and 4 of 5 with PRA. Plasma retinol-binding protein was identified in 1 spot and a fragment of albumin and plasma retinol-binding protein in the other. These proteins are candidate markers for diagnostic assays of AKI.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Assessment and prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with decompensated cirrhosis with serum cystatin C and urine N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jan;34(1):234-240. doi: 10.1111/jgh.14387. Epub 2018 Aug 21. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30062791
-
Urinary measurement of Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3 (NHE3) protein as new marker of tubule injury in critically ill patients with ARF.Am J Kidney Dis. 2003 Sep;42(3):497-506. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(03)00744-3. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003. PMID: 12955677
-
Diagnostic value of urine microscopy for differential diagnosis of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008 Nov;3(6):1615-9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02860608. Epub 2008 Sep 10. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008. PMID: 18784207 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury in Liver Disease: Role of Biomarkers.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015 Sep;22(5):368-75. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2015.06.009. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 26311598 Review.
-
Novel Biomarkers and Imaging Tests for Acute Kidney Injury Diagnosis in Patients with Cancer.Kidney360. 2025 Jan 1;6(1):167-174. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000000660. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Kidney360. 2025. PMID: 39575585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive analysis and annotation of human normal urinary proteome.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 8;7(1):3024. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-03226-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28596590 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between logistic regression and machine learning algorithms on prediction of noise-induced hearing loss and investigation of SNP loci.Sci Rep. 2025 May 2;15(1):15361. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00050-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40316545 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Significance of Urinary Retinol-Binding Protein 4: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 11;19(16):9878. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19169878. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36011513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation Between Tenofovir Drug Levels and the Renal Biomarkers RBP-4 and ß2M in the ION-4 Study Cohort.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019 Jan 24;6(1):ofy273. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofy273. eCollection 2019 Jan. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30697570 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Kininogen-1 and Retinol binding protein-4 respond to Acute Kidney Injury: predictors of patient prognosis?Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 21;6:19667. doi: 10.1038/srep19667. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26792617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Obialo CI, Okonofua EC, Tayade AS, Riley LJ. Epidemiology of De Novo Acute Renal Failure in Hospitalized African Americans: Comparing Community-Acquired Vs Hospital-Acquired Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2000;160:1309–1313. - PubMed
-
- Brivet FG, Kleinknecht DJ, Loirat P, Landais PJ. Acute Renal Failure in Intensive Care Units--Causes, Outcome, and Prognostic Factors of Hospital Mortality; a Prospective, Multicenter Study. French Study Group on Acute Renal Failure. Crit Care Med. 1996;24:192–198. - PubMed
-
- Liano F, Pascual J. Epidemiology of Acute Renal Failure: a Prospective, Multicenter, Community-Based Study. Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney Int. 1996;50:811–818. - PubMed
-
- Miller TR, Anderson RJ, Linas SL, Henrich WL, Berns AS, Gabow PA, Schrier RW. Urinary Diagnostic Indices in Acute Renal Failure: a Prospective Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1978;89:47–50. - PubMed
-
- Vaz AJ. Low Fractional Excretion of Urine Sodium in Acute Renal Failure Due to Sepsis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1983;143:738–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

