Neonatal Intracranial Ischemia and Hemorrhage : Role of Cranial Sonography and CT Scanning
- PMID: 20224705
- PMCID: PMC2836457
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2010.47.2.89
Neonatal Intracranial Ischemia and Hemorrhage : Role of Cranial Sonography and CT Scanning
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the role of cranial sonography and computed tomography in the diagnosis of neonatal intracranial hemorrhage and hypoxic-ischemic injury in an Indian set-up.
Methods: The study included 100 neonates who underwent cranial sonography and computed tomography (CT) in the first month of life for suspected intracranial ischemia and hemorrhage. Two observers rated the images for possible intracranial lesions and a kappa statistic for interobserver agreement was calculated.
Results: There was no significant difference in the kappa values of CT and ultrasonography (USG) for the diagnosis of germinal matrix hemorrhage/intraventricular hemorrhage (GMH/IVH) and periventricular leucomalacia (PVL) and both showed good interobserver agreement. USG, however detected more cases of GMH/IVH (24 cases) and PVL (19) cases than CT (22 cases and 16 cases of IVH and PVL, respectively). CT had significantly better interobserver agreement for the diagnosis of hypoxic ischemic injury (HII) in term infants and also detected more cases (33) as compared to USG (18). CT also detected 6 cases of extraaxial hemorrhages as compared to 1 detected by USG.
Conclusion: USG is better modality for imaging preterm neonates with suspected IVH or PVL. However, USG is unreliable in the imaging of term newborns with suspected HII where CT or magnetic resonance image scan is a better modality.
Keywords: CT-scan; Hypoxic ischemic injury; Ultrasonography.
Figures
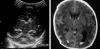
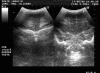
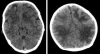
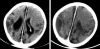
Similar articles
-
Sonography, CT, and MR imaging: a prospective comparison of neonates with suspected intracranial ischemia and hemorrhage.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000 Jan;21(1):213-8. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. PMID: 10669253 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neonatal intracranial ischemia and hemorrhage: diagnosis with US, CT, and MR imaging.Radiology. 1996 Apr;199(1):253-9. doi: 10.1148/radiology.199.1.8633155. Radiology. 1996. PMID: 8633155
-
Superficial Echogenic Lesions Detected on Neonatal Cranial Sonography: Possible Indicators of Severe Birth Injury.J Ultrasound Med. 2016 Mar;35(3):477-84. doi: 10.7863/ultra.15.04012. Epub 2016 Feb 2. J Ultrasound Med. 2016. PMID: 26839370
-
Pediatric neurosonography.J Child Neurol. 1986 Oct;1(4):319-37. doi: 10.1177/088307388600100403. J Child Neurol. 1986. PMID: 3298401 Review.
-
Preterm brain injury: Germinal matrix-intraventricular hemorrhage and post-hemorrhagic ventricular dilatation.Handb Clin Neurol. 2019;162:173-199. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64029-1.00008-4. Handb Clin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31324310 Review.
Cited by
-
Cinegraphic versus Combined Static and Cinegraphic Imaging for Initial Cranial Ultrasound Screening in Premature Infants.Pediatr Radiol. 2015 Oct;45(11):1706-11. doi: 10.1007/s00247-015-3382-0. Epub 2015 May 26. Pediatr Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26008871
-
Posterior Fossa Hemorrhage in a Term Neonate with Hemophilia A.J Med Ultrasound. 2018 Jan-Mar;26(1):56-58. doi: 10.4103/JMU.JMU_10_18. Epub 2018 Mar 28. J Med Ultrasound. 2018. PMID: 30065516 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of Brain Imaging with 3T MRI for Infants with History of Perinatal Hypoxia and their Comparison with 128 Slice NCCT Images.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Dec;16(Suppl 5):S4344-S4348. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_451_24. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 40061779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alan H, Volpe JJ. Hypoxic ischemic cerebral Injury in the Newborn. In: Kenneth FS, Stephan A, editors. Pediatr Neurol. ed 3. Vol 1. Mosby; 1999. pp. 191–204.
-
- Ayyapan C, Rajeswasri PA, Edwin N. Clinical and computerized tomography evaluation of term neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Indian Pediatr. 1999;36:174–177. - PubMed
-
- Babcock DS, Ball W., Jr Postasphyxial encephalopathy in full-term infants; ultrasound diagnosis. Radiology. 1983;148:417–423. - PubMed
-
- Boal DK, Watterberg KL, Miles S, Gifford KL. Optimal cost-effective timing of cranial ultrasound screening in low-birth weight infants. Pediatr Radiol. 1995;25:425–428. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

