miR-375 enhances palmitate-induced lipoapoptosis in insulin-secreting NIT-1 cells by repressing myotrophin (V1) protein expression
- PMID: 20224724
- PMCID: PMC2836503
miR-375 enhances palmitate-induced lipoapoptosis in insulin-secreting NIT-1 cells by repressing myotrophin (V1) protein expression
Abstract
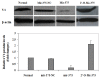
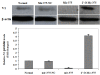
Lipoapoptosis of pancreatic beta cells caused by elevated circulating free fatty acids (FFAs) has now been recognized to be a pivotal factor contributing to beta cellular dysfunction and beta-mass lose in type 2 diabetes. Although recent studies suggested an important role for the ceramide pathway in the late destructive phase of lipid overload in the pancreatic beta cells, the overall underlying mechanisms leading to lipoapoptosis, however, remained poorly understood. mir-375 was recently characterized to be a pancreatic islet-specific miRNA implicated in the regulation of insulin secretion and beta-mass turnover. In the present study we further examined its effect on palmitate-induced lipoapoptosis in NIT-1 cells, a NOD-derived beta-cell line. It was found that NIT-1 cells with ectopic mir-375 expression were much more susceptible to palmitate-induced lipoapoptosis. In contrast, knockdown of endogenous pri-mir-375 expression by a modified antisense oligo, 2'-O-me-375, almost completely protected NIT-1 cells from palmitate-induced lipoapoptosis. We further demonstrated that mir-375 could target V1 mRNA and repress its translation. Consistent with this assumption, NIT-1 cells transfected with 2'-O-me-375 showed significant higher levels of V1 protein after palmitate induction. Together, our data suggest that mir-375 could be a potential therapeutic target for prevention and intervention of beta-cell dysfunction and beta-mass lose in type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Lipoapoptosis; NIT-1 cells; mir-375; type 2 diabetes; β-cell dysfunction; β-mass.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of G protein-coupled receptor 40 in lipoapoptosis in mouse beta-cell line NIT-1.J Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Jun;38(6):651-61. doi: 10.1677/JME-06-0048. J Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17556534
-
Cell death-inducing DFF45-like effector b (Cideb) is present in pancreatic beta-cells and involved in palmitate induced beta-cell apoptosis.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012 Feb;28(2):145-55. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.1295. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012. PMID: 21948526
-
The small RNA miR-375 - a pancreatic islet abundant miRNA with multiple roles in endocrine beta cell function.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Nov 15;456:95-101. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.02.043. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28254488 Review.
-
Pioglitazone attenuates fatty acid-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008 Jul;10(7):564-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00749.x. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. PMID: 17593232
-
An 'alpha-beta' of pancreatic islet microribonucleotides.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;88:208-219. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2017.01.009. Epub 2017 Jan 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28122254 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide analyses of radioresistance-associated miRNA expression profile in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using next generation deep sequencing.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 19;8(12):e84486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084486. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24367666 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Bcl-2 expression by miR-34a mediates palmitate-induced Min6 cells apoptosis.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:258695. doi: 10.1155/2014/258695. Epub 2014 Apr 14. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 24829923 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis and necrosis in the liver.Compr Physiol. 2013 Apr;3(2):977-1010. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c120020. Compr Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23720337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of microRNA-375 and its role as DNA epigenetic marker of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han population.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Dec 1;10(12):11986-11994. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966563 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic stress in the myocardium: adaptations of gene expression.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 Feb;55:130-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.06.008. Epub 2012 Jun 21. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 22728216 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Charles MA, Eschwege E, Thibult N, Claude JR, Warnet JM, Rosselin GE, Girard J, Balkau B. The role of non-esterified fatty acids in the deteriora tion of glucose tolerance in Caucasian subjects: results of the Paris Prospective Study. Diabetologia. 1997;40(9):1101–6. Sep; - PubMed
-
- Schulz LO, Bennett PH, Ravussin E, Kidd JR, Kidd KK, Esparza J, Valencia ME. Effects of traditional and western environments on prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians in Mexico and the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(8):1866–71. Aug; - PubMed
-
- Bluher M. Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009;117(6):241–50. Jun; - PubMed
-
- Surampudi PN, John-Kalarickal J, Fonseca VA. Emerging concepts in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mt Sinai J Med. 2009;76(3):216–26. Jun; - PubMed
-
- Davis N, Forges B, Wylie-Rosett J. Role of obesity and lifestyle interventions in the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. Minerva Med. 2009;100(3):221–8. Jun. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
