E2F-1 has dual roles depending on the cell cycle
- PMID: 20224733
- PMCID: PMC2836542
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6.116
E2F-1 has dual roles depending on the cell cycle
Abstract
The E2F family of transcription factors play a critical role in the control of cell proliferation. E2F-1 is the major cellular target of pRB and is regulated by pRB during cell proliferation. E2F-1-mediated activation and repression of target genes occurs in different settings. The role of E2F-1 and E2F-1/pRB complexes in regulation of different target genes, and in cycling versus quiescent cells, is unclear. In this study, effects of free E2F-1 (doesn't complex with pRb) and E2F-1/pRb complex, on E2F-1 target gene expression were compared in different cell growth conditions. Findings suggest that E2F-1 acts in different ways, not only depending on the target gene but also depending on different stages of the cell cycle. For example, E2F-1 acts as part of the repression complex with pRB in the expression of DHFR, b-myb, TK and cdc2 in asynchronously growing cells; on the other hand, E2F-1 acts as an activator in the expression of the same genes in cells that are re-entering the cycle.
Keywords: Cell cycle; E2F-1; Rb; TK; cdc2; cmyc; dhfr.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: There are no conflicts of interest and financial disclosure in the subject matter of this paper.
Figures
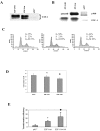
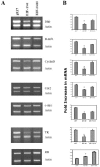
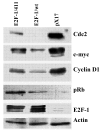



References
-
- Johnson DG, Ohtani K, Nevins JR. Autoregulatory control of E2F1 expression in response to positive and negative regulators of cell cycle progression. Genes Dev. 1994;8:1514–1525. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ. The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3689–3695. - PubMed
-
- Dyson N. The regulation of E2F by pRB-family proteins. Genes Dev. 1998;12:2245–2262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

