Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: important players in angiogenesis and tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 20224755
- PMCID: PMC2836134
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/135285
Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: important players in angiogenesis and tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
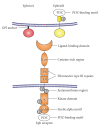
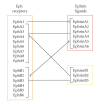
Eph receptors and their ephrin ligands were identified in the late 1980's. Subsequently, they were linked to different physiological and pathophysiological processes like embryonic development, angiogenesis, and tumorigenesis. In this regard, recent work focused on the distribution and effects of Eph receptors and ephrins on tumor cells and tumor microenvironment. The purpose of this review is to outline the role of these molecules in physiological angiogenesis and pathophysiological tumor angiogenesis. Furthermore, novel therapeutical approaches are discussed as Eph receptors and ephrins represent attractive targets for antiangiogenic therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of the ephrin and Eph receptor tyrosine kinase families in angiogenesis and development of the cardiovascular system.J Pathol. 2006 Mar;208(4):453-61. doi: 10.1002/path.1937. J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16470907 Review.
-
The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004 Dec;15(6):419-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.09.002. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004. PMID: 15561600 Review.
-
Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during angiogenesis and tumor progression.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Mar 10;312(5):642-50. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.10.028. Epub 2005 Dec 5. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16330025 Review.
-
The ephrins and Eph receptors in angiogenesis.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002 Feb;13(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(01)00031-4. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002. PMID: 11750881 Review.
-
Expression and function of the Eph A receptors and their ligands ephrins A in the rat thymus.J Immunol. 2002 Jul 1;169(1):177-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.1.177. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12077243
Cited by
-
Discovery and characterization of a novel cyclic peptide that effectively inhibits ephrin binding to the EphA4 receptor and displays anti-angiogenesis activity.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 12;8(11):e80183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080183. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24265799 Free PMC article.
-
EPH receptor/ephrin system: in the quest for novel anti-angiogenic therapies: Commentary on Hassan-Mohamed et al., Br J Pharmacol 171: 5195-5208.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Sep;172(18):4597-4599. doi: 10.1111/bph.12718. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 24724581 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Characterization of a Monobody with a Fibronectin Domain III Scaffold That Specifically Binds EphA2.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132976. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26177208 Free PMC article.
-
Angiogenesis: Managing the Culprits behind Tumorigenesis and Metastasis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2018 Mar 25;54(1):8. doi: 10.3390/medicina54010008. Medicina (Kaunas). 2018. PMID: 30344239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis.Nature. 2011 May 19;473(7347):298-307. doi: 10.1038/nature10144. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21593862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J, Takaku F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science. 1987;238(4834):1717–1720. - PubMed
-
- Brantley-Sieders D, Schmidt S, Parker M, Chen J. Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in tumor and tumor microenvironment. Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2004;10(27):3431–3442. - PubMed
-
- Zhou R. The Eph family receptors and ligands. Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 1998;77(3):151–181. - PubMed
-
- Kullander K, Klein R. Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2002;3(7):475–486. - PubMed
-
- Himanen J-P, Chumley MJ, Lackmann M, et al. Repelling class discrimination: ephrin-A5 binds to and activates EphB2 receptor signaling. Nature Neuroscience. 2004;7(5):501–509. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

