Rapidly evolving giant dermatofibroma
- PMID: 20224764
- PMCID: PMC2836174
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/620910
Rapidly evolving giant dermatofibroma
Abstract
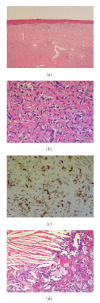
Dermatofibroma, also known as "fibrous histiocytoma", is a benign dermal or subcutaneous poorly circumscribed proliferation of spindle-shaped fibroblasts and macrophages in the dermis. Although it is commonly present as a brownish nodule the legs of females, it may also arise on the upper extremities, trunk, and rarely on the head. The exact pathogenesis is unclear. However, it is widely believed that the originating insult to the dermis is a folliculitis, an arthropod bite, or an unspecified initial inflammatory condition. Giant dermatofibromas of greater than 5 cm in diameter are rare, with only 22 cases reported in the literature. We present a case of a rapidly evolving pedunculated mass in the groin of a male patient. Histological examination confirmed this to be a giant dermatofibroma. Though this specimen cannot is not confirmed as such, the cellular subtype is sometimes present as a larger lesion with anecdotal reports of local recurrence and distant metastases. The clinical and radiological features which were somewhat suspicious of malignancy are considered in the context of the definitive pathological diagnosis of a benign lesion.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Giant hemosiderotic dermatofibroma: a case report and review of the literature.Case Rep Dermatol. 2011 Feb 18;3(1):32-6. doi: 10.1159/000324721. Case Rep Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21487458 Free PMC article.
-
Dermatofibroma.2024 Feb 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Feb 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 29262213 Free Books & Documents.
-
Giant dermatofibroma. A little-known clinical variant of dermatofibroma.J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994 May;30(5 Pt 1):714-8. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994. PMID: 8176009 Review.
-
Multiple cutaneous fibrous histiocytomas in association with systemic lupus erythematosus.J Dermatol. 2005 Aug;32(8):645-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2005.tb00815.x. J Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 16334865
-
[Giant dermatofibroma: case report and review of the literature].Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2007 Mar;98(2):121-4. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2007. PMID: 17397601 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Anterior Abdominal Wall Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: A Rare Case.Cureus. 2024 Aug 11;16(8):e66627. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66627. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39258060 Free PMC article.
-
A case of a giant lipidized dermatofibroma.JAAD Case Rep. 2025 Mar 22;61:116-118. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2025.02.041. eCollection 2025 Jul. JAAD Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40538790 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Giant hemosiderotic dermatofibroma: a case report and review of the literature.Case Rep Dermatol. 2011 Feb 18;3(1):32-6. doi: 10.1159/000324721. Case Rep Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21487458 Free PMC article.
-
Giant Muscle Invasive Dermatofibroma Clinically Mimicking a Malignant Tumor.Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2019 Mar 28;2019:4503272. doi: 10.1155/2019/4503272. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2019. PMID: 31049230 Free PMC article.
-
Plaque Like Giant Dermatofibroma: A Case Report.J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2017 Jan-Mar;10(1):51-53. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_117_16. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2017. PMID: 28529424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burns T, Griffiths C, Breathnach S, et al. Rook’s Textbook of Dermatology. 7th edition. Wiley Blackwell; 2004. Fibrohystiocytic tumours.
-
- Rapini RP. Practical Dermatopathology. Mosby; 2005. Fibrohistiocytic proliferations and neoplasms.
-
- Hueso L, Sanmartín Jiménez O, Alfaro-Rubio A, et al. Giant dermatofibroma: case report and review of the literature. Actas Dermo-Sifiliograficas. 2007;98(2):121–124. - PubMed
-
- Zelger B, Zelger BG, Burgdorf WHC. Dermatofibroma: a critical evaluation. International Journal of Surgical Pathology. 2004;12(4):333–344. - PubMed
-
- Calonje E. Dermatofibroma (fibrous histiocytoma): an inflammatory or neoplastic disorder? Histopathology. 2001;39(2):p. 213. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

