Abnormalities in signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy
- PMID: 20224802
- PMCID: PMC2834210
- DOI: 10.1586/eem.09.70
Abnormalities in signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy
Abstract
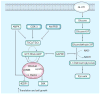
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is characterized by a plethora of signaling abnormalities that together ultimately result in the clinical and pathologic hallmarks of DN, namely progressive albuminuria followed by a gradual decline in glomerular filtration rate leading to kidney failure, and accompanied by podocyte loss, progressive glomerular sclerosis and, ultimately, progressive tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Over the past few years, the general understanding of the abnormalities in signaling pathways that lead to DN has expanded considerably. In this review, some of the important pathways that appear to be involved in driving this process are discussed, with special emphasis on newer findings and insights. Newer concepts regarding signaling changes in bradykinin, mTOR, JAK/STAT, MCP-1, VEGF, endothelial nitric oxide synthase, activated protein C and other pathways are discussed.
Figures

References
-
-
Pagtalunan ME, Miller PL, Jumping-Eagle S, et al. Podocyte loss and progressive glomerular injury in Type II diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1997;99(2):342–348.. • First study to demonstrate that podocyte depletion was an important feature of diabetic nephropathy (DN) that predicted progressive DN.
-
-
- Wharram BL, Goyal M, Wiggins JE, et al. Podocyte depletion causes glomerulosclerosis: diphtheria toxin-induced podocyte depletion in rats expressing human diphtheria toxin receptor transgene. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(10):2941–2952. - PubMed
-
- Meyer TW, Bennett PH, Nelson RG. Podocyte number predicts long-term urinary albumin excretion in Pima Indians with Type II diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetologia. 1999;42(11):1341–1344. - PubMed
-
- Morcos M, Borcea V, Isermann B, et al. Effect of α-lipoic acid on the progression of endothelial cell damage and albuminuria in patients with diabetes mellitus: an exploratory study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2001;52(3):175–183. - PubMed
-
- Isermann B, Vinnikov IA, Madhusudhan T, et al. Activated protein C protects against diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting endothelial and podocyte apoptosis. Nat Med. 2007;13(11):1349–1358. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
