Anthranilate-activating modules from fungal nonribosomal peptide assembly lines
- PMID: 20225828
- PMCID: PMC2854178
- DOI: 10.1021/bi100198y
Anthranilate-activating modules from fungal nonribosomal peptide assembly lines
Abstract
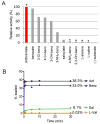
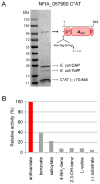
Fungal natural products containing benzodiazepinone- and quinazolinone-fused ring systems can be assembled by nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) using the conformationally restricted beta-amino acid anthranilate as one of the key building blocks. We validated that the first module of the acetylaszonalenin synthetase of Neosartorya fischeri NRRL 181 activates anthranilate to anthranilyl-AMP. With this as a starting point, we then used bioinformatic predictions about fungal adenylation domain selectivities to identify and confirm an anthranilate-activating module in the fumiquinazoline A producer Aspergillus fumigatus Af293 as well as a second anthranilate-activating NRPS in N. fischeri. This establishes an anthranilate adenylation domain code for fungal NRPS and should facilitate detection and cloning of gene clusters for benzodiazepine- and quinazoline-containing polycyclic alkaloids with a wide range of biological activities.
Figures
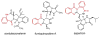




References
-
- D’Yakonov A, Telezhenetskaya M. Quinazoline alkaloids in nature. Chem Nat Compd. 1997;33:221–267.
-
- Finking R, Marahiel MA. Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2004;58:453–488. - PubMed
-
- Sattely ES, Fischbach MA, Walsh CT. Total biosynthesis: in vitro reconstitution of polyketide and nonribosomal peptide pathways. Nat Prod Rep. 2008;25:757–793. - PubMed
-
- Yeulet SE, Mantle PG. Biosynthesis of auranthine by Penicillium aurantiogriseum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1987;41:207–210.
-
- Houck DR, et al. On the biosynthesis of asperlicin and the directed biosynthesis of analogs in Aspergillus alliaceus. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1988;41:882–891. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

