Logic-based models for the analysis of cell signaling networks
- PMID: 20225868
- PMCID: PMC2853906
- DOI: 10.1021/bi902202q
Logic-based models for the analysis of cell signaling networks
Abstract
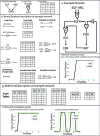
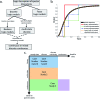
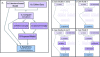
Computational models are increasingly used to analyze the operation of complex biochemical networks, including those involved in cell signaling networks. Here we review recent advances in applying logic-based modeling to mammalian cell biology. Logic-based models represent biomolecular networks in a simple and intuitive manner without describing the detailed biochemistry of each interaction. A brief description of several logic-based modeling methods is followed by six case studies that demonstrate biological questions recently addressed using logic-based models and point to potential advances in model formalisms and training procedures that promise to enhance the utility of logic-based methods for studying the relationship between environmental inputs and phenotypic or signaling state outputs of complex signaling networks.
Figures
References
-
- Kestler H. A.; Wawra C.; Kracher B.; Kuhl M. (2008) Network modeling of signal transduction: Establishing the global view. BioEssays 30, 1110–1125. - PubMed
-
- Heinrichs A., Kritikou E., Pulverer B., and Raftopoulou M., Eds. (2006) Systems biology: A user's guide, Nature Publishing Group, New York.
-
- Janes K. A.; Lauffenburger D. A. (2006) A biological approach to computational models of proteomic networks. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 10, 73–80. - PubMed
-
- Ideker T.; Lauffenburger D. (2003) Building with a scaffold: Emerging strategies for high- to low-level cellular modeling. Trends Biotechnol. 21, 255–262. - PubMed
-
- Aldridge B. B.; Burke J. M.; Lauffenburger D. A.; Sorger P. K. (2006) Physicochemical modelling of cell signalling pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 1195–1203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

