The RST and PARP-like domain containing SRO protein family: analysis of protein structure, function and conservation in land plants
- PMID: 20226034
- PMCID: PMC2848248
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-170
The RST and PARP-like domain containing SRO protein family: analysis of protein structure, function and conservation in land plants
Abstract
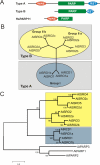
Background: The SROs (SIMILAR TO RCD-ONE) are a group of plant-specific proteins which have important functions in stress adaptation and development. They contain the catalytic core of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) domain and a C-terminal RST (RCD-SRO-TAF4) domain. In addition to these domains, several, but not all, SROs contain an N-terminal WWE domain.
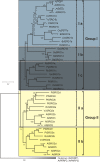
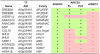
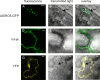
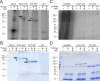
Results: SROs are present in all analyzed land plants and sequence analysis differentiates between two structurally distinct groups; cryptogams and monocots possess only group I SROs whereas eudicots also contain group II. Group I SROs possess an N-terminal WWE domain (PS50918) but the WWE domain is lacking in group II SROs. Group I domain structure is widely represented in organisms as distant as humans (for example, HsPARP11). We propose a unified nomenclature for the SRO family. The SROs are able to interact with transcription factors through the C-terminal RST domain but themselves are generally not regulated at the transcriptional level. The most conserved feature of the SROs is the catalytic core of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PS51059) domain. However, bioinformatic analysis of the SRO PARP domain fold-structure and biochemical assays of AtRCD1 suggested that SROs do not possess ADP-ribosyl transferase activity.
Conclusions: The SROs are a highly conserved family of plant specific proteins. Sequence analysis of the RST domain implicates a highly preserved protein structure in that region. This might have implications for functional conservation. We suggest that, despite the presence of the catalytic core of the PARP domain, the SROs do not possess ADP-ribosyl transferase activity. Nevertheless, the function of SROs is critical for plants and might be related to transcription factor regulation and complex formation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genome-wide characterization of a SRO gene family involved in response to biotic and abiotic stresses in banana (Musa spp.).BMC Plant Biol. 2019 May 22;19(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1807-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31113386 Free PMC article.
-
Plant PARPs, PARGs and PARP-like Proteins.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016;17(7):713-723. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160419144721. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016. PMID: 27090905 Review.
-
A special member of the rice SRO family, OsSRO1c, mediates responses to multiple abiotic stresses through interaction with various transcription factors.Plant Mol Biol. 2014 Apr;84(6):693-705. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0163-8. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Plant Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24337801
-
Arabidopsis SIMILAR TO RCD-ONE genes are ubiquitous and respond to multiple abiotic stresses through diverse signaling pathways.J Biosci. 2019 Dec;44(6):129. J Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31894110
-
The PARP superfamily.Bioessays. 2004 Aug;26(8):882-93. doi: 10.1002/bies.20085. Bioessays. 2004. PMID: 15273990 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification of SIMILAR to RCD ONE (SRO) gene family in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) reveals their role in drought stress response.Plant Signal Behav. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):2379128. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2024.2379128. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Plant Signal Behav. 2024. PMID: 39003725 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerases in Host-Pathogen Interactions, Inflammation, and Immunity.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018 Dec 19;83(1):e00038-18. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00038-18. Print 2019 Mar. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2018. PMID: 30567936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous protein mono-ADP-ribosylation in Arabidopsis thaliana.Planta. 2011 Jun;233(6):1287-92. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1415-y. Epub 2011 Apr 26. Planta. 2011. PMID: 21519881
-
Morpho-physiological and molecular characterization of drought tolerance traits in Gossypium hirsutum genotypes under drought stress.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020 Dec;26(12):2339-2353. doi: 10.1007/s12298-020-00890-3. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2020. PMID: 33424151 Free PMC article.
-
Noncanonical mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation of zinc finger SZF proteins counteracts ubiquitination for protein homeostasis in plant immunity.Mol Cell. 2021 Nov 18;81(22):4591-4604.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.09.006. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34592134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jaspers P, Blomster T, Brosché M, Salojärvi J, Ahlfors R, Vainonen JP, Reddy RA, Immink R, Angenent G, Turck F, Overmyer K, Kangasjärvi J. Unequally redundant RCD1 and SRO1 mediate stress and developmental responses and interact with transcription factors. Plant J. 2009;60(2):268–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03951.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Overmyer K, Tuominen H, Kettunen R, Betz C, Langebartels C, Sandermann H, Kangasjärvi J. Ozone-sensitive Arabidopsis rcd1 mutant reveals opposite roles for ethylene and jasmonate signaling pathways in regulating superoxide-dependent cell death. Plant Cell. 2000;12(10):1849–62. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.10.1849. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahlfors R, Lång S, Overmyer K, Jaspers P, Brosché M, Tauriainen A, Kollist H, Tuominen H, Belles-Boix E, Piippo M, Inzé D, Palva ET, Kangasjärvi J. Arabidopsis RADICAL-INDUCED CELL DEATH1 belongs to the WWE protein-protein interaction domain protein family and modulates abscisic acid, ethylene, and methyl jasmonate responses. Plant Cell. 2004;16(7):1925–37. doi: 10.1105/tpc.021832. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

