Influence of 5 major Salmonella pathogenicity islands on NK cell depletion in mice infected with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis
- PMID: 20226037
- PMCID: PMC2848020
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-75
Influence of 5 major Salmonella pathogenicity islands on NK cell depletion in mice infected with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis
Abstract
Background: In this study we were interested in the colonisation and early immune response of Balb/C mice to infection with Salmonella Enteritidis and isogenic pathogenicity island free mutants.
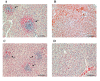
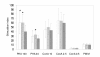
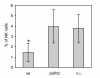
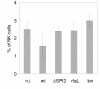
Results: The virulence of S. Enteritidis for Balb/C mice was exclusively dependent on intact SPI-2. Infections with any of the mutants harbouring SPI-2 (including the mutant in which we left only SPI-2 but removed SPI-1, SPI-3, SPI-4 and SPI-5) resulted in fatalities, liver injures and NK cell depletion from the spleen. The infection was of minimal influence on counts of splenic CD4 CD8 T lymphocytes and gammadelta T-lymphocytes although a reduced ability of splenic lymphocytes to respond to non-specific mitogens indicated general immunosuppression in mice infected with SPI-2 positive S. Enteritidis mutants. Further investigations showed that NK cells were depleted also in blood but not in the caecal lamina propria. However, NK cell depletion was not directly associated with the presence of SPI-2 and was rather an indicator of virulence or avirulence of a particular mutant because the depletion was not observed in mice infected with other attenuated mutants such as lon and rfaL.
Conclusions: The virulence of S. Enteritidis for Balb/C mice is exclusively dependent on the presence of SPI-2 in its genome, and a major hallmark of the infection in terms of early changes in lymphocyte populations is the depletion of NK cells in spleen and blood. The decrease of NK cells in circulation can be used as a marker of attenuation of S. Enteritidis mutants for Balb/C mice.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Virulence potential of five major pathogenicity islands (SPI-1 to SPI-5) of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis for chickens.BMC Microbiol. 2009 Dec 19;9:268. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-268. BMC Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 20021686 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of sodCI and spvBC in Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis reduced its virulence to the natural virulence of serovars Agona, Hadar and Infantis for mice but not for chickens early after infection.Vet Microbiol. 2009 Nov 18;139(3-4):304-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.06.023. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Vet Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19595520
-
Infection of mice by Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis involves additional genes that are absent in the genome of serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2012 Feb;80(2):839-49. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05497-11. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22083712 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Enteritidis Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 type III secretion system: role in intestinal colonization of chickens and systemic spread.Microbiology (Reading). 2010 Sep;156(Pt 9):2770-2781. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.038018-0. Epub 2010 May 20. Microbiology (Reading). 2010. PMID: 20488876
-
Evaluation of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis pathogenicity island-1 proteins as vaccine candidates against S. Enteritidis challenge in chickens.Vet Microbiol. 2011 Mar 24;148(2-4):298-307. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.09.006. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Vet Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 20888713
Cited by
-
SPI-1-encoded type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica is required for the suppression of porcine alveolar macrophage cytokine expression.Vet Res. 2011 Jan 24;42(1):16. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-16. Vet Res. 2011. PMID: 21314975 Free PMC article.
-
Diet-induced obese mice exhibit altered immune responses to early Salmonella Typhimurium oral infection.J Microbiol. 2018 Sep;56(9):673-682. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-8083-6. Epub 2018 Aug 23. J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30141160
-
Mainstreams of horizontal gene exchange in enterobacteria: consideration of the outbreak of enterohemorrhagic E. coli O104:H4 in Germany in 2011.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025702. Epub 2011 Oct 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22022434 Free PMC article.
-
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a Salmonella Enteritidis sptP mutant as a live attenuated vaccine candidate.BMC Vet Res. 2017 Jun 24;13(1):194. doi: 10.1186/s12917-017-1115-3. BMC Vet Res. 2017. PMID: 28646853 Free PMC article.
-
Composition of Gut Microbiota Influences Resistance of Newly Hatched Chickens to Salmonella Enteritidis Infection.Front Microbiol. 2016 Jun 17;7:957. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00957. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27379083 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

