Differential gene expression in human granulosa cells from recombinant FSH versus human menopausal gonadotropin ovarian stimulation protocols
- PMID: 20226040
- PMCID: PMC2842272
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7827-8-25
Differential gene expression in human granulosa cells from recombinant FSH versus human menopausal gonadotropin ovarian stimulation protocols
Abstract
Background: The study was designed to test the hypothesis that granulosa cell (GC) gene expression response differs between recombinant FSH and human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG) stimulation regimens.
Methods: Females < 35 years-old undergoing IVF for tubal or male factor infertility were prospectively randomized to one of two stimulation protocols, GnRH agonist long protocol plus individualized dosages of (1) recombinant (r)FSH (Gonal-F) or (2) purified human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG; Menopur). Oocytes were retrieved 35 h post-hCG, and GC were collected. Total RNA was extracted from each GC sample, biotinylated cRNA was synthesized, and each sample was run on Human Genome Bioarrays (Applied Microarrays). Unnamed genes and genes with <2-fold difference in expression were excluded.
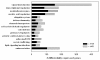
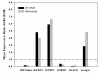
Results: After exclusions, 1736 genes exhibited differential expression between groups. Over 400 were categorized as signal transduction genes, approximately 180 as transcriptional regulators, and approximately 175 as enzymes/metabolic genes. Expression of selected genes was confirmed by RT-PCR. Differentially expressed genes included A kinase anchor protein 11 (AKAP11), bone morphogenetic protein receptor II (BMPR2), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP)-4, IGFBP-5, and hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha.
Conclusions: Results suggest that major differences exist in the mechanism by which pure FSH alone versus FSH/LH regulate gene expression in preovulatory GC that could impact oocyte maturity and developmental competence.
Figures
References
-
- Keye WR, Webster B, Dickey R, Somkuti S, Crain J, Scobey MJ. Subcuteneously administered Menopur®, a new highly purified human menopausal gonadotropin, causes significantly fewer injection site reactions than Repronex® in subjects undergoing in vitro fertilization. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2005;3:62–67. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-3-62. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frydman R, Howles CM, Truong F. A double-blind, randomized study to compare recombinant human follicle stimulating hormone (FSH; Gonal-F) with highly purified urinary FSH (Metrodin HP) in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques including intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod. 2000;15:520–525. doi: 10.1093/humrep/15.3.520. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lenton E, Soltan A, Hewitt J, Thomson A, Davies W, Ashraf N, Sharma V, Jenner L, Ledger W, McVeigh E. Induction of ovulation in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques: recombinant human FSH (follitrophin alpha) versus highly purified urinary FSH (urofollitrophin HP) Hum Reprod. 2000;15:1021–7. doi: 10.1093/humrep/15.5.1021. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

