Ginger DNA transposons in eukaryotes and their evolutionary relationships with long terminal repeat retrotransposons
- PMID: 20226081
- PMCID: PMC2836005
- DOI: 10.1186/1759-8753-1-3
Ginger DNA transposons in eukaryotes and their evolutionary relationships with long terminal repeat retrotransposons
Abstract
Background: In eukaryotes, long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons such as Copia, BEL and Gypsy integrate their DNA copies into the host genome using a particular type of DDE transposase called integrase (INT). The Gypsy INT-like transposase is also conserved in the Polinton/Maverick self-synthesizing DNA transposons and in the 'cut and paste' DNA transposons known as TDD-4 and TDD-5. Moreover, it is known that INT is similar to bacterial transposases that belong to the IS3, IS481, IS30 and IS630 families. It has been suggested that LTR retrotransposons evolved from a non-LTR retrotransposon fused with a DNA transposon in early eukaryotes. In this paper we analyze a diverse superfamily of eukaryotic cut and paste DNA transposons coding for INT-like transposase and discuss their evolutionary relationship to LTR retrotransposons.
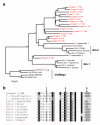
Results: A new diverse eukaryotic superfamily of DNA transposons, named Ginger (for 'Gypsy INteGrasE Related') DNA transposons is defined and analyzed. Analogously to the IS3 and IS481 bacterial transposons, the Ginger termini resemble those of the Gypsy LTR retrotransposons. Currently, Ginger transposons can be divided into two distinct groups named Ginger1 and Ginger2/Tdd. Elements from the Ginger1 group are characterized by approximately 40 to 270 base pair (bp) terminal inverted repeats (TIRs), and are flanked by CCGG-specific or CCGT-specific target site duplication (TSD) sequences. The Ginger1-encoded transposases contain an approximate 400 amino acid N-terminal portion sharing high amino acid identity to the entire Gypsy-encoded integrases, including the YPYY motif, zinc finger, DDE domain, and, importantly, the GPY/F motif, a hallmark of Gypsy and endogenous retrovirus (ERV) integrases. Ginger1 transposases also contain additional C-terminal domains: ovarian tumor (OTU)-like protease domain or Ulp1 protease domain. In vertebrate genomes, at least two host genes, which were previously thought to be derived from the Gypsy integrases, apparently have evolved from the Ginger1 transposase genes. We also introduce a second Ginger group, designated Ginger2/Tdd, which includes the previously reported DNA transposon TDD-4.
Conclusions: The Ginger superfamily represents eukaryotic DNA transposons closely related to LTR retrotransposons. Ginger elements provide new insights into the evolution of transposable elements and certain transposable element (TE)-derived genes.
Figures

References
-
- Eickbush T, Malik H. In: Mobile DNA II. Craig NL, Craigie R, Gellert M, Lambowitz AM, editor. Washington, DC, USA: American Society for Microbiology Press; 2002. Origins and evolution of retrotransposons; pp. 1111–1144.
-
- Jurka J, Kapitonov VV. First cryptons from invertebrates. Repbase Rep. 2008;8:232–233.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

