Zolpidem modulation of phasic and tonic GABA currents in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- PMID: 20226798
- PMCID: PMC2860024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.03.003
Zolpidem modulation of phasic and tonic GABA currents in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
Abstract
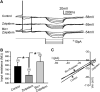
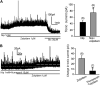
Zolpidem is a widely prescribed sleep aid with relative selectivity for GABA(A) receptors containing alpha1-3 subunits. We examined the effects of zolpidem on the inhibitory currents mediated by GABA(A) receptors using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from DMV neurons in transverse brainstem slices from rat. Zolpidem prolonged the decay time of mIPSCs and of muscimol-evoked whole-cell GABAergic currents, and it occasionally enhanced the amplitude of mIPSCs. The effects were blocked by flumazenil, a benzodiazepine antagonist. Zolpidem also hyperpolarized the resting membrane potential, with a concomitant decrease in input resistance and action potential firing activity in a subset of cells. Zolpidem did not clearly alter the GABA(A) receptor-mediated tonic current (I(tonic)) under baseline conditions, but after elevating extracellular GABA concentration with nipecotic acid, a non-selective GABA transporter blocker, zolpidem consistently and significantly increased the tonic GABA current. This increase was suppressed by flumazenil and gabazine. These results suggest that alpha1-3 subunits are expressed in synaptic GABA(A) receptors on DMV neurons. The baseline tonic GABA current is likely not mediated by these same low affinity, zolpidem-sensitive GABA(A) receptors. However, when the extracellular GABA concentration is increased, zolpidem-sensitive extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors containing alpha1-3 subunits contribute to the I(tonic).
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



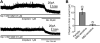
Similar articles
-
Multiple types of GABAA receptors mediate inhibition in brain stem parasympathetic cardiac neurons in the nucleus ambiguus.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Dec;96(6):3266-72. doi: 10.1152/jn.00590.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 16. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16914614
-
Functional and molecular plasticity of γ and α1 GABAA receptor subunits in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus after experimentally induced diabetes.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Nov 1;118(5):2833-2841. doi: 10.1152/jn.00085.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 23. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28835522 Free PMC article.
-
Subtype-specific GABA transporter antagonists synergistically modulate phasic and tonic GABAA conductances in rat neocortex.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Sep;94(3):2073-85. doi: 10.1152/jn.00520.2005. Epub 2005 Jun 29. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15987761
-
Propofol and isoflurane enhancement of tonic gamma-aminobutyric acid type a current in cardiac vagal neurons in the nucleus ambiguus.Anesth Analg. 2009 Jan;108(1):142-8. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e31818d8b79. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19095842
-
Tonic GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition in the rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Feb;103(2):904-14. doi: 10.1152/jn.00511.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 16. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20018836 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Zolpidem is a potent stoichiometry-selective modulator of α1β3 GABAA receptors: evidence of a novel benzodiazepine site in the α1-α1 interface.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 27;6:28674. doi: 10.1038/srep28674. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27346730 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic and extrasynaptic transmission of kidney-related neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Dec;110(11):2637-47. doi: 10.1152/jn.00155.2013. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 24027107 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced astroglial GABA uptake attenuates tonic GABAA inhibition of the presympathetic hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons in heart failure.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Aug;114(2):914-26. doi: 10.1152/jn.00080.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 10. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26063771 Free PMC article.
-
Function of the GABAergic System in Diabetic Encephalopathy.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Mar;43(2):605-619. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01214-7. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 35460435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perinatal high fat diet increases inhibition of dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus neurons regulating gastric functions.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018 Jan;30(1):10.1111/nmo.13150. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13150. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018. PMID: 28762595 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai D, Zhu G, Pennefather P, Jackson MF, MacDonald JF, Orser BA. Distinct functional and pharmacological properties of tonic and quantal inhibitory postsynaptic currents mediated by gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors in hippocampal neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;59:814–824. - PubMed
-
- Barnard EA, Skolnick P, Olsen RW, Mohler H, Sieghart W, Biggio G, Braestrup C, Bateson AN, Langer SZ. International Union of Pharmacology. XV. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors: classification on the basis of subunit structure and receptor function. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998;50:291–313. - PubMed
-
- Bouairi E, Kamendi H, Wang X, Gorini C, Mendelowitz D. Multiple types of GABAA receptors mediate inhibition in brain stem parasympathetic cardiac neurons in the nucleus ambiguus. J. Neurophysiol. 2006;96:3266–3272. - PubMed
-
- Broussard DL, Li H, Altschuler SM. Colocalization of GABA(A) and NMDA receptors within the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMV) of the rat. Brain Res. 1997;763:123–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

