NOD2 contributes to the inflammatory responses of primary murine microglia and astrocytes to Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 20226841
- PMCID: PMC2859426
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.03.013
NOD2 contributes to the inflammatory responses of primary murine microglia and astrocytes to Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
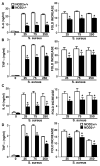
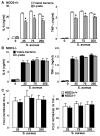
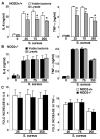
We have recently demonstrated that microglia and astrocytes express nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-2 (NOD2), a novel cytosolic pattern recognition receptor for bacterial motifs, and we have shown that this intracellular receptor is essential for glial responses to Gram-negative pathogens. Here, we demonstrate that intact Staphylococcus aureus, a major Gram-positive causative agent of brain abscesses, activates the transcription factor NF-kappaB and is a potent stimulus for inflammatory cytokine production in primary murine microglia and astrocytes. Interestingly, we demonstrate that NOD2 is essential for maximal glial responses to intact S. aureus, but not cellular lysates. As such, this data indicates that NOD2 plays an important role in initiating inflammatory mediator production by resident brain cells following S. aureus infection and we suggest that this cytosolic receptor acts in conjunction with cell surface pattern recognition receptors to elicit maximal glial responses.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
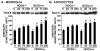
References
-
- Brandenburg LO, Varoga D, Nicolaeva N, Leib SL, Wilms H, Podschun R, Wruck CJ, Schröder JM, Pufe T, Lucius R. Role of glial cells in the functional expression of LL-37/rat cathelin-related antimicrobial peptide in meningitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008;67:1041–1054. - PubMed
-
- Bowman CC, Rasley A, Tranguch SL, Marriott I. Cultured astrocytes express toll-like receptors for bacterial products. Glia. 2003;43:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Bsibsi M, Ravid R, Gveric D, van Noort JM. Broad expression of Toll-like receptors in the human central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2002;61:1013–1021. - PubMed
-
- Calfee DP, Wispelwey B. Brain abscess. Semin Neurol. 2000;20:353–360. - PubMed
-
- Carpentier PA, Begolka WS, Olson JK, Elhofy A, Karpus WJ, Miller SD. Differential activation of astrocytes by innate and adaptive immune stimuli. Glia. 2005;49:360–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

