d-Dimer and CRP levels are elevated prior to antiretroviral treatment in patients who develop IRIS
- PMID: 20227921
- PMCID: PMC2892199
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clim.2010.02.010
d-Dimer and CRP levels are elevated prior to antiretroviral treatment in patients who develop IRIS
Erratum in
- Clin Immunol. 2010 Sep;136(3):462
Abstract
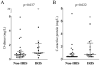
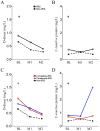
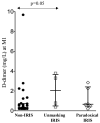
Biomarkers could be useful in evaluating immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). A cohort of 45 HIV-1-infected, antiretroviral treatment (ART)-naive patients with baseline CD4 T cell counts <or=100 cells/microL who were started on ART, suppressed HIV-RNA to <50 copies/mL, and seen every 1-3 months for 1 year were retrospectively evaluated for suspected or confirmed IRIS. d-Dimer, C-reactive protein (CRP), and selected autoantibodies were analyzed at baseline, 1 and 3 months post-ART in cryopreserved plasma. Median differences between cases and controls were compared with Mann-Whitney and Fisher's exact tests. Sixteen patients (35.6%) developed IRIS (median of 35 days post-ART initiation): unmasking=8, paradoxical=7, autoimmune=1. Pre-ART d-dimer and CRP were higher in IRIS cases versus controls (d-dimer: 0.89 mg/L versus 0.66 mg /L, p=0.037; CRP: 0.74 mg/L versus 0.39 mg/L, p=0.022), while d-dimer was higher in unmasking cases at IRIS onset (2.04 mg/L versus 0.36 mg /L, p=0.05). These biomarkers may be useful in identifying patients at risk for IRIS.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Higher levels of CRP, D-dimer, IL-6, and hyaluronic acid before initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) are associated with increased risk of AIDS or death.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 1;203(11):1637-46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir134. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21592994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interleukin-2 cycling causes transient increases in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and D-dimer that are not associated with plasma HIV-RNA levels.AIDS. 2009 Sep 24;23(15):2015-9. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832d72c6. AIDS. 2009. PMID: 19617815 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after antiretroviral therapy initiation in patients with tuberculosis: findings from the SAPiT trial.Ann Intern Med. 2012 Sep 4;157(5):313-24. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-5-201209040-00004. Ann Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 22944873 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HIV & immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS).Indian J Med Res. 2011 Dec;134(6):866-77. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.92632. Indian J Med Res. 2011. PMID: 22310819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers in immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: signals from pathogenesis.Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2010 Nov;5(6):504-10. doi: 10.1097/COH.0b013e32833ed774. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2010. PMID: 20966640 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plasma IL-6/IL-10 Ratio and IL-8, LDH, and HBDH Level Predict the Severity and the Risk of Death in AIDS Patients with Pneumocystis Pneumonia.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:1583951. doi: 10.1155/2016/1583951. Epub 2016 Aug 7. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27579328 Free PMC article.
-
Paradoxical tuberculosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB-IRIS) in HIV patients with culture confirmed pulmonary tuberculosis in India and the potential role of IL-6 in prediction.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e63541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063541. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691062 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Elevated frequencies of highly activated CD4+ T cells in HIV+ patients developing immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome.Blood. 2010 Nov 11;116(19):3818-27. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-05-285080. Epub 2010 Jul 26. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20660788 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Decreases in colonic and systemic inflammation in chronic HIV infection after IL-7 administration.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Jan 30;10(1):e1003890. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003890. eCollection 2014 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24497828 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transient expansion of activated CD8(+) T cells characterizes tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in patients with HIV: a case control study.J Inflamm (Lond). 2013 May 20;10:21. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-10-21. eCollection 2013. J Inflamm (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23688318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- French MA, Price P, Stone SF. Immune restoration disease after antiretroviral therapy. AIDS. 2004;18:1615–27. - PubMed
-
- Shelburne SA, 3rd, Hamill RJ. The immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. AIDS Rev. 2003;5:67–79. - PubMed
-
- Lipman M, Breen R. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2006;19:20–5. - PubMed
-
- Lawn SD, Lipman MC, Easterbrook PJ. Immune reconstitution disease associated with mycobacterial infections. Curr Opin HIV AIDS. 2008;3:425–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

