Beta-arrestin 2 is required for B1 receptor-dependent post-translational activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
- PMID: 20228252
- PMCID: PMC2887266
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-148783
Beta-arrestin 2 is required for B1 receptor-dependent post-translational activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase
Abstract
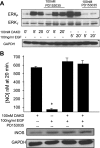
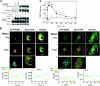
A major source of "high-output" NO in inflammation is inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). iNOS is primarily transcriptionally regulated and is thought to function as an uncontrolled generator of high NO. We found that iNOS in cytokine-stimulated human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVECs) is highly regulated post-translationally via activation of the B1 kinin G protein-coupled receptor (B1R). We report here that B1R-mediated iNOS activation was significantly inhibited by knockdown of beta-arrestin 2 with siRNA in cytokine-treated HLMVECs or HEK293 cells transfected with iNOS and B1R. In contrast, beta-arrestin 1 siRNA had no effect. The prolonged phase of B1R-dependent ERK activation was also inhibited by beta-arrestin 2 knockdown. Furthermore, robust ERK activation by the epidermal growth factor receptor (a beta-arrestin 2 independent pathway) had no effect on iNOS-derived NO production. beta-arrestin 2 and iNOS coimmunoprecipitated, and there was significant fluorescence resonance energy transfer between CFP-iNOS and beta-arrestin 2-YFP (but not beta-arrestin 1-YFP) that increased 3-fold after B1R stimulation. These data show that beta-arrestin 2 mediates B1R-dependent high-output NO by scaffolding iNOS and ERK to allow post-translational activation of iNOS. This could play a critical role in mediating endothelial function in inflammation.
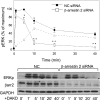
Figures
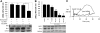
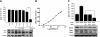
Similar articles
-
A novel pathway for receptor-mediated post-translational activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase.J Cell Mol Med. 2011 Feb;15(2):258-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00992.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 20015194 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic receptor-dependent activation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase by ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Ser745.J Biol Chem. 2007 Nov 2;282(44):32453-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706242200. Epub 2007 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17804409
-
Differential regulation of inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthase by kinin B1 and B2 receptors.Neuropeptides. 2010 Apr;44(2):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.12.004. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Neuropeptides. 2010. PMID: 20045558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Arrestin-1 protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress/p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis-mediated apoptosis via repressing p-p65/inducible nitric oxide synthase in portal hypertensive gastropathy.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Oct;87:69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26119788
-
Carboxypeptidase M augments kinin B1 receptor signaling by conformational crosstalk and enhances endothelial nitric oxide output.Biol Chem. 2013 Mar;394(3):335-45. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0290. Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23183746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kinin-stimulated B1 receptor signaling depends on receptor endocytosis whereas B2 receptor signaling does not.Neurochem Res. 2014 Jun;39(6):1037-47. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1126-9. Epub 2013 Aug 10. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 23934212
-
Effects of Post-translational Modifications on Membrane Localization and Signaling of Prostanoid GPCR-G Protein Complexes and the Role of Hypoxia.J Membr Biol. 2019 Oct;252(4-5):509-526. doi: 10.1007/s00232-019-00091-4. Epub 2019 Sep 4. J Membr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31485700 Review.
-
Nitric Oxide and S-Nitrosylation in Cardiac Regulation: G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase-2 and β-Arrestins as Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 7;22(2):521. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020521. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33430208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling.Pharmacol Rev. 2017 Jul;69(3):256-297. doi: 10.1124/pr.116.013367. Pharmacol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28626043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterologous down-regulation of angiotensin type 1 receptors by purinergic P2Y2 receptor stimulation through S-nitrosylation of NF-kappaB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Apr 19;108(16):6662-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017640108. Epub 2011 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21464294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kubes P. Nitric oxide affects microvascular permeability in the intact and inflamed vasculature. Microcirculation. 1995;2:235–244. - PubMed
-
- Schubert W, Frank P G, Woodman S E, Hyogo H, Cohen D E, Chow C W, Lisanti M P. Microvascular hyperpermeability in caveolin-1 (−/−) knock-out mice. Treatment with a specific nitric-oxide synthase inhibitor, L-NAME, restores normal microvascular permeability in Cav-1 null mice. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:40091–40098. - PubMed
-
- Predescu D, Predescu S, Shimizu J, Miyawaki-Shimizu K, Malik A B. Constitutive eNOS-derived nitric oxide is a determinant of endothelial junctional integrity. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;289:L371–L381. - PubMed
-
- Papapetropoulos A, Rudic R D, Sessa W C. Molecular control of nitric oxide synthases in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;43:509–520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

