Octopamine promotes rhythmicity but not synchrony in a bilateral pair of bursting motor neurons in the feeding circuit of Aplysia
- PMID: 20228355
- PMCID: PMC2837736
- DOI: 10.1242/jeb.040378
Octopamine promotes rhythmicity but not synchrony in a bilateral pair of bursting motor neurons in the feeding circuit of Aplysia
Abstract
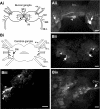
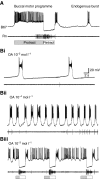
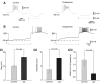
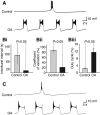
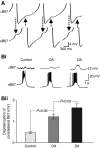
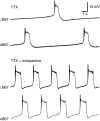
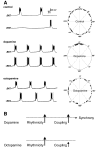
Octopamine-like immunoreactivity was localized to a limited number (<40) of neurons in the Aplysia central nervous system, including three neurons in the paired buccal ganglia (BG) that control feeding movements. Application of octopamine (OA) to the BG circuit produced concentration-dependent (10(-8)-10(-4) mol l(-1)) modulatory actions on the spontaneous burst activity of the bilaterally paired B67 pharyngeal motor neurons (MNs). OA increased B67's burst duration and the number of impulses per burst. These effects reflected actions of OA on the intrinsic tetrodotoxin-resistant driver potential (DP) that underlies B67 bursting. In addition to its effects on B67's burst parameters, OA also increased the rate and regularity of burst timing. Although the bilaterally paired B67 MNs both exhibited rhythmic bursting in the presence of OA, they did not become synchronized. In this respect, the response to OA differed from that of dopamine, another modulator of the feeding motor network, which produces both rhythmicity and synchrony of bursting in the paired B67 neurons. It is proposed that modulators can regulate burst synchrony of MNs by exerting a dual control over their intrinsic rhythmicity and their reciprocal capacity to generate membrane potential perturbations. In this simple system, dopaminergic and octopaminergic modulation could influence whether pharyngeal contractions occur in a bilaterally synchronous or asynchronous fashion.
Figures


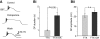

References
-
- Benson J. A. (1984). Octopamine alters rhythmic activity in the isolated cardiac ganglion of the crab, Portunus sanguinolentus. Neurosci. Lett. 44, 59-64 - PubMed
-
- Berry M. D. (2007). The potential of trace amines and their receptors for treating neurological and psychiatric diseases. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2, 3-19 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

