Three-dimensional tissue culture based on magnetic cell levitation
- PMID: 20228788
- PMCID: PMC4487889
- DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2010.23
Three-dimensional tissue culture based on magnetic cell levitation
Abstract
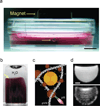
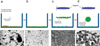
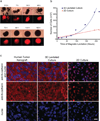
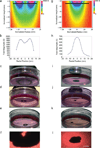
Cell culture is an essential tool in drug discovery, tissue engineering and stem cell research. Conventional tissue culture produces two-dimensional cell growth with gene expression, signalling and morphology that can be different from those found in vivo, and this compromises its clinical relevance. Here, we report a three-dimensional tissue culture based on magnetic levitation of cells in the presence of a hydrogel consisting of gold, magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and filamentous bacteriophage. By spatially controlling the magnetic field, the geometry of the cell mass can be manipulated, and multicellular clustering of different cell types in co-culture can be achieved. Magnetically levitated human glioblastoma cells showed similar protein expression profiles to those observed in human tumour xenografts. Taken together, these results indicate that levitated three-dimensional culture with magnetized phage-based hydrogels more closely recapitulates in vivo protein expression and may be more feasible for long-term multicellular studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center (UTMDACC) and Rice University (RU), along with their researchers, have filled patents on the technology and other intellectual property reported here. If licensing or commercialization occurs, the researchers will be entitled to standard royalties. G.R.S., R.M.R., C.S.L., and T.C.K. have equity in Nano3D Biosciences, Inc. UTMDACC and RU manage the terms of these arrangements in accordance to their established institutional conflict-of-interest policies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A simple cell patterning method using magnetic particle-containing photosensitive poly (ethylene glycol) hydrogel blocks: a technical note.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011 Aug;17(8):871-7. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2010.0690. Epub 2011 May 25. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011. PMID: 21486199
-
Magnetic levitating polymeric nano/microparticular substrates for three-dimensional tumor cell culture.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011 Jul 1;85(2):379-84. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.02.021. Epub 2011 Feb 21. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011. PMID: 21420837
-
Numerical Simulation of Mass Transfer and Three-Dimensional Fabrication of Tissue-Engineered Cartilages Based on Chitosan/Gelatin Hybrid Hydrogel Scaffold in a Rotating Bioreactor.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2017 Jan;181(1):250-266. doi: 10.1007/s12010-016-2210-9. Epub 2016 Aug 15. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27526111
-
Formation of a three-dimensional multicellular assembly using magnetic patterning.Langmuir. 2009 Feb 17;25(4):2348-54. doi: 10.1021/la8030792. Langmuir. 2009. PMID: 19166275
-
Magnetic 3D cell culture: State of the art and current advances.Life Sci. 2021 Dec 1;286:120028. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120028. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34627776 Review.
Cited by
-
Complex 3D bioprinting methods.APL Bioeng. 2021 Mar 11;5(1):011508. doi: 10.1063/5.0034901. eCollection 2021 Mar. APL Bioeng. 2021. PMID: 33728391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phage display for the detection, analysis, disinfection, and prevention of Staphylococcus aureus.Smart Med. 2022 Dec 23;1(1):e20220015. doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20220015. eCollection 2022 Dec. Smart Med. 2022. PMID: 39188734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A scaffold-free surface culture of B16F10 murine melanoma cells based on magnetic levitation.Cytotechnology. 2016 Dec;68(6):2323-2334. doi: 10.1007/s10616-016-0026-7. Epub 2016 Sep 26. Cytotechnology. 2016. PMID: 27670438 Free PMC article.
-
Digital microfabrication of user-defined 3D microstructures in cell-laden hydrogels.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2013 Nov;110(11):3038-47. doi: 10.1002/bit.24957. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2013. PMID: 23686741 Free PMC article.
-
Drug screening of biopsy-derived spheroids using a self-generated microfluidic concentration gradient.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 2;8(1):14672. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33055-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30279484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cukierman E, Pankov R, Stevens DR, Yamada KM. Taking cell-matrix adhesions to the third dimension. Science. 2001;294:1708–1712. - PubMed
-
- Abbott A. Biology's new dimension. Nature. 2003;424:870–872. - PubMed
-
- Pampaloni F, Reynaud EG, Stelzer EH. The third dimension bridges the gap between cell culture and live tissue. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:839–845. - PubMed
-
- Griffith LG, Swartz MA. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:211–224. - PubMed
-
- Atala A. Engineering tissues, organs and cells. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007;1:83–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

