An intravascular immune response to Borrelia burgdorferi involves Kupffer cells and iNKT cells
- PMID: 20228796
- PMCID: PMC5114121
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1855
An intravascular immune response to Borrelia burgdorferi involves Kupffer cells and iNKT cells
Abstract
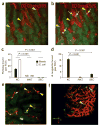
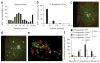
Here we investigate the dynamics of the hepatic intravascular immune response to a pathogen relevant to invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT cells). Immobilized Kupffer cells with highly ramified extended processes into multiple sinusoids could effectively capture blood-borne, disseminating Borrelia burgdorferi, creating a highly efficient surveillance and filtering system. After ingesting B. burgdorferi, Kupffer cells induced chemokine receptor CXCR3-dependent clustering of iNKT cells. Kupffer cells and iNKT cells formed stable contacts via the antigen-presenting molecule CD1d, which led to iNKT cell activation. An absence of iNKT cells caused B. burgdorferi to leave the blood and enter the joints more effectively. B. burgdorferi that escaped Kupffer cells entered the liver parenchyma and survived despite Ito cell responses. Kupffer cell-iNKT cell interactions induced a key intravascular immune response that diminished the dissemination of B. burgdorferi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



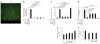

References
-
- Auffray C, et al. Monitoring of blood vessels and tissues by a population of monocytes with patrolling behavior. Science. 2007;317:666–670. - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg M. Toward an understanding of NKT cell biology: progress and paradoxes. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:877–900. - PubMed
-
- Kawano T, et al. CD1d-restricted and TCR-mediated activation of Vα14 NKT cells by glycosylceramides. Science. 1997;278:1626–1629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

