CD169(+) macrophages present lipid antigens to mediate early activation of iNKT cells in lymph nodes
- PMID: 20228797
- PMCID: PMC2923071
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1853
CD169(+) macrophages present lipid antigens to mediate early activation of iNKT cells in lymph nodes
Abstract
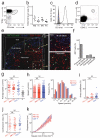
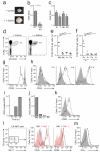
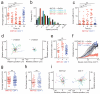
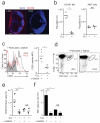
Invariant natural killer T cells (iNKT cells) are involved in the host defense against microbial infection. Although it is known that iNKT cells recognize glycolipids presented by CD1d, how and where they encounter antigen in vivo remains unclear. Here we used multiphoton microscopy to visualize the dynamics and activation of iNKT cells in lymph nodes. After antigen administration, iNKT cells became confined in a CD1d-dependent manner in close proximity to subcapsular sinus CD169(+) macrophages. These macrophages retained, internalized and presented lipid antigen and were required for iNKT cell activation, cytokine production and population expansion. Thus, CD169(+) macrophages can act as true antigen-presenting cells controlling early iNKT cell activation and favoring the fast initiation of immune responses.
Figures


References
-
- Cerundolo V, Silk J, Masri SH, Salio M. Harnessing invariant NKT cells in vaccination strategies. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:28–38. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A, Savage PB, Teyton L. The biology of NKT cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:297–336. - PubMed
-
- Brigl M, Brenner MB. CD1: antigen presentation and T cell function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:817–890. - PubMed
-
- Kinjo Y, et al. Natural killer T cells recognize diacylglycerol antigens from pathogenic bacteria. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:978–986. - PubMed
-
- Kinjo Y, et al. Recognition of bacterial glycosphingolipids by natural killer T cells. Nature. 2005;434:520–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

