PHF6 mutations in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 20228800
- PMCID: PMC2847364
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.542
PHF6 mutations in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
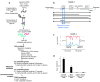
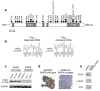
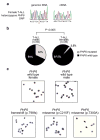
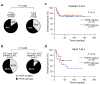
Tumor suppressor genes on the X chromosome may skew the gender distribution of specific types of cancer. T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematological malignancy with an increased incidence in males. In this study, we report the identification of inactivating mutations and deletions in the X-linked plant homeodomain finger 6 (PHF6) gene in 16% of pediatric and 38% of adult primary T-ALL samples. Notably, PHF6 mutations are almost exclusively found in T-ALL samples from male subjects. Mutational loss of PHF6 is importantly associated with leukemias driven by aberrant expression of the homeobox transcription factor oncogenes TLX1 and TLX3. Overall, these results identify PHF6 as a new X-linked tumor suppressor in T-ALL and point to a strong genetic interaction between PHF6 loss and aberrant expression of TLX transcription factors in the pathogenesis of this disease.
Figures
References
-
- Carrel L, Willard HF. X-inactivation profile reveals extensive variability in X-linked gene expression in females. Nature. 2005;434:400–404. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg JM, et al. Childhood T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute acute lymphoblastic leukemia consortium experience. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3616–3622. - PubMed
-
- Aifantis I, Raetz E, Buonamici S. Molecular pathogenesis of T-cell leukaemia and lymphoma. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:380–390. - PubMed
-
- Pui CH, Robison LL, Look AT. Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 2008;371:1030–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

