Mesolimbic dopamine reward system hypersensitivity in individuals with psychopathic traits
- PMID: 20228805
- PMCID: PMC2916168
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2510
Mesolimbic dopamine reward system hypersensitivity in individuals with psychopathic traits
Abstract
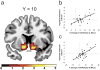
Psychopathy is a personality disorder that is strongly linked to criminal behavior. Using [(18)F]fallypride positron emission tomography and blood oxygen level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging, we found that impulsive-antisocial psychopathic traits selectively predicted nucleus accumbens dopamine release and reward anticipation-related neural activity in response to pharmacological and monetary reinforcers, respectively. These findings suggest that neurochemical and neurophysiological hyper-reactivity of the dopaminergic reward system may comprise a neural substrate for impulsive-antisocial behavior and substance abuse in psychopathy.
Figures
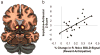
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

