Biphasic effects of sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aorta
- PMID: 20228827
- PMCID: PMC4007672
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2010.24
Biphasic effects of sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aorta
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aortic ring.
Methods: Thoracic aortae from normal rats were isolated and equilibrated in organ bath with Krebs-Henseleit buffer and ring tension was recorded. Effects of sodium danshensu on basal tonus of the vessel and its effects on vessel contraction and relaxation with or without endothelium were observed.
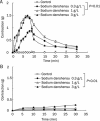
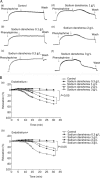
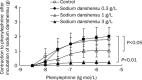
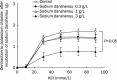
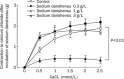
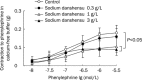
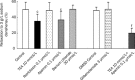
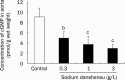
Results: In thoracic arteries under basal tonus, sodium danshensu (0.3-3 g/L) produced a dose-dependent transient contraction. In phenylephrine-precontracted thoracic arteries with or without endothelium, low concentration (0.1-0.3 g/L) of sodium danshensu produced a weak contraction, while high concentrations (1-3 g/L) produced a pronounced vasodilator after a transient vasocontraction. Pre-incubation with sodium danshensu could inhibit vessel contraction induced by phenylephrine and potassium chloride in a concentration-dependent way. Sodium danshensu inhibited phenylephrine- and CaCl(2)-induced vasoconstriction in Ca(2+)-free medium. Pre-incubation with tetraethylammonium, a non-selective K(+) channel blocker, and apamin, a small-conductance calcium-activated K(+) channel blocker partially antagonized the relaxation response induced by sodium danshensu. However, iberiotoxin (big-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channel blocker), barium chloride (inward rectifier K(+) channel blocker), and glibencalmide (ATP-sensitive K(+) channel blocker) had no influence on the vasodilation effect of sodium danshensu.
Conclusion: Sodium danshensu showed a biphasic effects on vessel tension. While low dosage of sodium danshensu produced small contraction possibly through transient enhancement of Ca(2+) influx, high dosage produced significant vasodilation mainly through promoting the opening of non-selective K(+) channels and small-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channels in the vascular smooth muscle cells.
Figures
References
-
- Ji XY, Tan BK, Zhu YZ. Salvia miltiorrhiza and ischemic diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2000;21:1089–94. - PubMed
-
- Dong ZT, Jiang WD. Effect of danshensu on isolated swine coronary artery perfusion preparation. Acta Pharm Sin. 1982;17:226–8. - PubMed
-
- Lam FFY, Yeung JHK, Chan KM, Or PMY. Relaxant effects of danshen aqueous extract and its constituent danshensu on rat coronary artery are mediated by inhibition of calcium channels. Vasc Pharmacol. 2007;46:271–7. - PubMed
-
- Gu YH, Zhang CY, Huang GQ, Wang ZY. Effects of Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae and its component “danshensu” on the anticoagulant and fibrinolytic functions of cultured bovine endothetial cells. Acta Univ Med Secondae Shanghai. 1990;10:208–12.
-
- Wu L, Qiao H, Li Y, Li L. Protective roles of puerarin and Danshensu on acute ischemic myocardial injury in rats. Phytomedicine. 2007;14:652–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

