Viral hepatocarcinogenesis
- PMID: 20228847
- PMCID: PMC3148694
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.36
Viral hepatocarcinogenesis
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Despite recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of HCC, its prognosis remains dismal. Infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) are the major risk factors for HCC. Although both are hepatotropic viral infections, there are important differences between the oncogenic mechanisms of these two viruses. In addition to the oncogenic potential of its viral proteins, HBV, as a DNA virus, can integrate into host DNA and directly transform hepatocytes. In contrast, HCV, an RNA virus, is unable to integrate into the host genome, and viral protein expression has a more critical function in hepatocarcinogenesis. Both HBV and HCV proteins have been implicated in disrupting cellular signal transduction pathways that lead to unchecked cell growth. Most HCC develops in the cirrhotic liver, but the linkage between cirrhosis and HCC is likely multifactorial. In this review, we summarize current knowledge regarding the pathogenetic mechanisms of viral HCC.
Figures


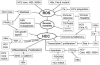
References
-
- Adinolfi LE, Gambardella M, Andreana A, Tripodi MF, Utili R, Ruggiero G. Steatosis accelerates the progression of liver damage of chronic hepatitis C patients and correlates with specific HCV genotype and visceral obesity. Hepatology. 2001;33:1358–1364. - PubMed
-
- Alisi A, Giambartolomei S, Cupelli F, Merlo P, Fontemaggi G, Spaziani A, et al. Physical and functional interaction between HCV core protein and the different p73 isoforms. Oncogene. 2003;22:2573–2580. - PubMed
-
- Anzola M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: role of hepatitis B and hepaititis C viruses proteins in hepatocarcinogenesis. J Viral Hepat. 2004;11:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Aravalli RN, Steer CJ, Cressman ENK. Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2008;48:2047–2063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

