Local IGF-1 isoform protects cardiomyocytes from hypertrophic and oxidative stresses via SirT1 activity
- PMID: 20228935
- PMCID: PMC2837204
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100107
Local IGF-1 isoform protects cardiomyocytes from hypertrophic and oxidative stresses via SirT1 activity
Abstract
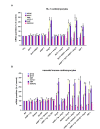
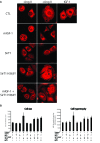
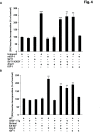
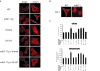
Oxidative and hypertrophic stresses contribute to the pathogenesis of heart failure. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) is a peptide hormone with a complex post-transcriptional regulation, generating distinct isoforms. Locally acting IGF-1 isoform (mIGF-1) helps the heart to recover from toxic injury and from infarct. In the murine heart, moderate overexpression of the NAD(+)-dependent deacetylase SirT1 was reported to mitigate oxidative stress. SirT1 is known to promote lifespan extension and to protect from metabolic challenges. Circulating IGF-1 and SirT1 play antagonizing biological roles and share molecular targets in the heart, in turn affecting cardiomyocyte physiology. However, how different IGF-1 isoforms may impact SirT1 and affect cardiomyocyte function is unknown. Here we show that locally acting mIGF-1 increases SirT1 expression/activity, whereas circulating IGF-1 isoform does not affect it, in cultured HL-1 and neonatal cardiomyocytes. mIGF-1-induced SirT1 activity exerts protection against angiotensin II (Ang II)-triggered hypertrophy and against paraquat (PQ) and Ang II-induced oxidative stress. Conversely, circulating IGF-1 triggered itself oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Interestingly, potent cardio-protective genes (adiponectin, UCP-1 and MT-2) were increased specifically in mIGF-1-overexpressing cardiomyocytes, in a SirT1-dependent fashion. Thus, mIGF-1 protects cardiomyocytes from oxidative and hypertrophic stresses via SirT1 activity, and may represent a promising cardiac therapeutic.
Keywords: IGF-1; SirT1; cardiomyocytes; cell hypertrophy; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article report no conflict of interests.
Figures

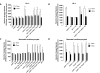

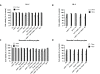
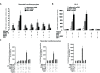
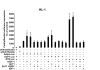
Comment in
-
Surprising sirtuin crosstalk in the heart.Aging (Albany NY). 2010 Mar 31;2(3):129-32. doi: 10.18632/aging.100128. Aging (Albany NY). 2010. PMID: 20375467 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
mIGF-1/JNK1/SirT1 signaling confers protection against oxidative stress in the heart.Aging Cell. 2012 Feb;11(1):139-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00766.x. Epub 2011 Dec 11. Aging Cell. 2012. PMID: 22051242
-
Cardioprotective mIGF-1/SIRT1 signaling induces hypertension, leukocytosis and fear response in mice.Aging (Albany NY). 2012 Jun;4(6):402-16. doi: 10.18632/aging.100464. Aging (Albany NY). 2012. PMID: 22691943 Free PMC article.
-
The TRPA1 channel is a cardiac target of mIGF-1/SIRT1 signaling.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Oct 1;307(7):H939-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00150.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25108014
-
Emerging roles of SIRT1 deacetylase in regulating cardiomyocyte survival and hypertrophy.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011 Oct;51(4):614-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.01.008. Epub 2011 Jan 27. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21276800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Sirtuin 1 in the Growth Hormone/Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Signal Transduction and Its Impact on Growth Processes in Children.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 20;24(20):15406. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015406. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895086 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Mechanical Loading Variations on the Hypertrophic, Anti-Apoptotic, and Anti-Inflammatory Responses of Differentiated Cardiomyocyte-like H9C2 Cells.Cells. 2022 Jan 29;11(3):473. doi: 10.3390/cells11030473. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159283 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory Effect of Myokines on Reactive Oxygen Species in Ischemia/Reperfusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 9;21(24):9382. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249382. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33317180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac aging and insulin resistance: could insulin/insulin-like growth factor (IGF) signaling be used as a therapeutic target?Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(32):5684-94. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319320004. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective role of ErbB3 signaling in myeloid cells during adaptation to cardiac pressure overload.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021 Mar;152:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.11.009. Epub 2020 Nov 28. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33259856 Free PMC article.
-
Locally expressed IGF1 propeptide improves mouse heart function in induced dilated cardiomyopathy by blocking myocardial fibrosis and SRF-dependent CTGF induction.Dis Model Mech. 2012 Jul;5(4):481-91. doi: 10.1242/dmm.009456. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Dis Model Mech. 2012. PMID: 22563064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frey N, Olson EN. Cardiac hypertrophy: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Annu Rev Physiol. 2003;65:45–79. - PubMed
-
- Takimoto E, Kass DA. Role of oxidative stress in cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling. Hypertension. 2007;49:241–248. - PubMed
-
- Lavu S, Boss O, Elliott PJ, Lambert PD. Sirtuins--novel therapeutic targets to treat age-associated diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:841–853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
