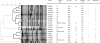Prevalence and clonality of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the Atlantic Azores islands: predominance of SCCmec types IV, V and VI
- PMID: 20229224
- PMCID: PMC2854357
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-010-0892-4
Prevalence and clonality of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the Atlantic Azores islands: predominance of SCCmec types IV, V and VI
Abstract
In order to obtain insights into the methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) population structure in the Azores archipelago, 106 MRSA isolates were collected from patients attending an Azorean central hospital between January 2007 and February 2008. Antimicrobial resistance was determined for all isolates. Molecular typing was performed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), spa typing, multilocus sequence typing (MLST), staphylococcal chromosome cassette mec (SCCmec) typing and the presence of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL). The majority of the isolates (87%, n = 92) belonged to the EMRSA-15 clone (ST22, SCCmec-IVh), followed by the Pediatric clone (ST5-VI/IVc) (11%, n = 12). The Berlin clone (ST45-IVa) and a new clone (spa type t1839, ST1339 and SCCmec V variant) were represented by single isolates. All of the isolates carried SCCmec types IV, V or VI and a non-multiresistant antibiotic profile, resembling the currently emerging community MRSA. Moreover, PVL was described for the first time to be associated with the Pediatric clone carrying SCCmec type VI. We provided the first description of the population structure of MRSA in the Azores islands, which seems to be shaped by genetic events occurring locally, as well as by the regular population exchange between the islands, continental Portugal, the United Kingdom and the United States.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from the Arkhangelsk region, Russia: antimicrobial susceptibility, molecular epidemiology, and distribution of Panton-Valentine leukocidin genes.APMIS. 2008 Oct;116(10):877-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2008.01092.x. APMIS. 2008. PMID: 19132981
-
Molecular characteristics of community-acquired, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Chinese children.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010 Apr;58(3):356-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00648.x. Epub 2010 Jan 28. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20132304
-
Molecular analysis and susceptibility patterns of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains circulating in the community in the Ligurian area, a northern region of Italy: emergence of USA300 and EMRSA-15 clones.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009 Nov;34(5):424-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.06.016. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009. PMID: 19651493
-
The evolution of Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Genet Evol. 2008 Dec;8(6):747-63. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2008.07.007. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Infect Genet Evol. 2008. PMID: 18718557 Review.
-
Community-associated meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children in Taiwan, 2000s.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011 Jul;38(1):2-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2011.01.011. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2011. PMID: 21397461 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in nosocomial infections in a tertiary-care facility: emergence of new clonal complexes in Saudi Arabia.New Microbes New Infect. 2016 Jul 29;14:13-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2016.07.009. eCollection 2016 Nov. New Microbes New Infect. 2016. PMID: 27621823 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Instrumented Nucleic Acid Amplification (NINA) for Rapid Detection of Ralstonia solanacearum Race 3 Biovar 2.Biol Eng Trans. 2011;4(2):69-80. doi: 10.13031/2013.38508. Biol Eng Trans. 2011. PMID: 25485176 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in HIV patients: risk factors associated with colonization and/or infection and methods for characterization of isolates - a systematic review.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014 Nov;69(11):770-6. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2014(11)11. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2014. PMID: 25518036 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of MRSA strains isolated from patients in a hospital in Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.BMC Microbiol. 2012 Jul 23;12:146. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-146. BMC Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22823982 Free PMC article.
-
A field guide to pandemic, epidemic and sporadic clones of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 6;6(4):e17936. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017936. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21494333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (2009) EARSS annual report 2008. EARSS, Bilthoven, The Netherlands. Available online at: http://www.rivm.nl/earss/Images/EARSS%202008_final_tcm61-65020.pdf, pp 55–58
-
- Nübel U, Roumagnac P, Feldkamp M, Song JH, Ko KS, Huang YC, Coombs G, Ip M, Westh H, Skov R, Struelens MJ, Goering RV, Strommenger B, Weller A, Witte W, Achtman M. Frequent emergence and limited geographic dispersal of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(37):14130–14135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804178105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical