Reverse shoulder arthroplasty as a salvage procedure for failed conventional shoulder replacement due to cuff failure--midterm results
- PMID: 20229269
- PMCID: PMC3014498
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-010-0990-z
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty as a salvage procedure for failed conventional shoulder replacement due to cuff failure--midterm results
Abstract
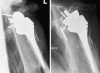
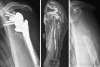
Our goal was to evaluate the objective and subjective midterm outcome after revision of a failed shoulder arthroplasty with a reverse design prosthesis. Twenty consecutive patients with 21 revisions of a primary shoulder arthroplasty using reverse shoulder prosthesis Delta III(®) were followed up postoperatively for a mean of 46 months including clinical and radiological examination. Complications were recorded and Constant score, DASH and SF36 were assessed. With the numbers given a significant reduction of pain was achieved from 8.7 to 3.0 (p < 0.001). There was a significant improvement of active flexion from 43° to 97° (p < 0.001) and active abduction from 44° to 90° (p < 0.001). However, at the same time, active external rotation with an adducted humerus decreased significantly from 26° to 12° (p = 0.012). The constant score improved significantly from 16.7 to 55.9 (p < 0.001). Sixteen patients (84%) rated their shoulder better or much better than before. In 43% an intraoperative and in 38% a postoperative complication occurred including two late stage infections which required prosthesis removal. Our results support the use of the reverse prosthesis as revision prosthesis. The reverse design helps to compensate functional deficits due to severe soft-tissue damage except active external rotation. Nevertheless, the revision is a technically demanding procedure reflected in a high rate of intraoperative complications. The rate of secondary infections of 10% remains a special concern.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Comparison and Correlation of Clinical Outcome Metrics in Anatomic and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty.Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2015 Dec;73 Suppl 1:S118-23. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013). 2015. PMID: 26631207
-
The use of the reverse shoulder prosthesis for the treatment of failed hemiarthroplasty for proximal humeral fracture.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007 Feb;89(2):292-300. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.E.01310. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007. PMID: 17272443
-
Neer Award 2005: The Grammont reverse shoulder prosthesis: results in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006 Sep-Oct;15(5):527-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2006.01.003. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006. PMID: 16979046
-
Use of the reverse shoulder prosthesis for the treatment of failed hemiarthroplasty in patients with glenohumeral arthritis and rotator cuff deficiency.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007 Feb;89(2):189-95. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.89B2.18161. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007. PMID: 17322433 Review.
-
[Shoulder arthroplasty].Ugeskr Laeger. 2006 May 8;168(19):1841-4. Ugeskr Laeger. 2006. PMID: 16756797 Review. Danish.
Cited by
-
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty, Deltopectoral Approach vs. Anterosuperior Approach: An Overview of the Literature.Front Surg. 2021 Nov 18;8:721054. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.721054. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2021. PMID: 34869550 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative complications during revision shoulder arthroplasty: a study using the National Joint Registry dataset.Shoulder Elbow. 2017 Apr;9(2):92-99. doi: 10.1177/1758573216685706. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Shoulder Elbow. 2017. PMID: 28405220 Free PMC article.
-
A convertible shoulder system: is it useful in total shoulder arthroplasty revisions?Int Orthop. 2015 Feb;39(2):299-304. doi: 10.1007/s00264-014-2563-z. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Int Orthop. 2015. PMID: 25319947
-
Humeral socket decoupling from the stem causes mechanical failure of a reverse shoulder prosthesis. A case report.JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2025 Feb 14;5(2):283-287. doi: 10.1016/j.xrrt.2025.01.010. eCollection 2025 May. JSES Rev Rep Tech. 2025. PMID: 40321879 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical and radiological outcome of the Total Evolutive Shoulder System (TESS®) reverse shoulder arthroplasty: a prospective comparative non-randomised study.Int Orthop. 2014 May;38(5):1001-6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-013-2277-7. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Int Orthop. 2014. PMID: 24458592 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Baulot E, Chabernaud D, Grammont PM. Results of Grammont’s inverted prosthesis in omarthritis associated with major cuff destruction. Apropos of 16 cases. Acta Orthop Belg. 1995;61(Suppl 1):112–119. - PubMed
-
- Boileau P, Chuinard C, Roussanne Y, Bicknell RT, Rochet N, Trojani C. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty combined with a modified latissimus dorsi and teres major tendon transfer for shoulder pseudoparalysis associated with dropping arm. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(3):584–593. doi: 10.1007/s11999-008-0114-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

