Targeting CXCR1/CXCR2 receptor antagonism in malignant melanoma
- PMID: 20230195
- PMCID: PMC4229031
- DOI: 10.1517/14728221003652471
Targeting CXCR1/CXCR2 receptor antagonism in malignant melanoma
Abstract
Importance of the field: The incidence of malignant melanoma is increasing throughout the world and is currently rising faster than any other cancer in men and second only to lung cancer in women. Current strategies focused on systemic therapy for treatment of melanoma have shown no effect on survival. Therefore there is a pressing need for developing novel targeted therapeutics.
Areas covered in this review: Our goal is to provide an overview regarding targeting CXCR1/2 in malignant melanoma, the rationale behind these approaches and the future perspective.
What the reader will gain: This review illustrates our current understanding of CXCR1/2 receptor in melanoma progression and metastasis. We describe approaches that are being developed to block CXCR1/2 activation, including low-molecular-weight antagonists, modified chemokines and antibodies directed against ligands and receptors.
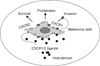
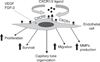
Take home message: The chemokine receptors CXCR1 and CXCR2 and their ligands play an important role in the pathogenesis of malignant melanoma. Recent reports demonstrated that CXCR1 is constitutively expressed in all melanoma cases irrespective of stage and grade, however, CXCR2 expression was restricted to aggressive melanoma tumors,. Furthermore, modulation of CXCR1/2 expression and/or activity has been shown to regulate malignant melanoma growth, angiogenesis and metastasis, suggesting CXCR1/2 targeting as a novel therapeutic approach for malignant melanoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ladarixin, a dual CXCR1/2 inhibitor, attenuates experimental melanomas harboring different molecular defects by affecting malignant cells and tumor microenvironment.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):14428-14442. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14803. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28129639 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR1/2 antagonism with CXCL8/Interleukin-8 analogue CXCL8(3-72)K11R/G31P restricts lung cancer growth by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and suppressing angiogenesis.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 28;6(25):21315-27. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4066. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26087179 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule antagonists for CXCR2 and CXCR1 inhibit human colon cancer liver metastases.Cancer Lett. 2011 Jan 28;300(2):180-8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.10.004. Epub 2010 Oct 29. Cancer Lett. 2011. PMID: 21035946 Free PMC article.
-
Combined anti CXC receptors 1 and 2 therapy is a promising anti-inflammatory treatment for respiratory diseases by reducing neutrophil migration and activation.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Oct;34:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26271598 Review.
-
CXCL8 and its cognate receptors in melanoma progression and metastasis.Future Oncol. 2010 Jan;6(1):111-6. doi: 10.2217/fon.09.128. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20021212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: ADAMs control inflammation from afar.J Leukoc Biol. 2015 Mar;97(3):437-8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3CE1114-528R. J Leukoc Biol. 2015. PMID: 25733375 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR2 inhibition overcomes ponatinib intolerance by eradicating chronic myeloid leukemic stem cells through PI3K/Akt/mTOR and dipeptidylpeptidase Ⅳ (CD26).Heliyon. 2023 Nov 9;9(11):e22091. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22091. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38045173 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus lipid factors modulate melanoma cell clustering and invasion.Dis Model Mech. 2024 Sep 1;17(9):dmm050770. doi: 10.1242/dmm.050770. Epub 2024 Sep 16. Dis Model Mech. 2024. PMID: 39284707 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine CXCL1 may serve as a potential molecular target for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2016 Oct;5(10):2861-2871. doi: 10.1002/cam4.843. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27682863 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of CXC-Chemokine Receptor 1 Expression in Chorioamnionitis Is Associated with Adverse Perinatal Outcomes.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 1;12(4):882. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040882. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35453930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, et al. International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:145–176. - PubMed
-
- Zlotnik A, Yoshie O. Chemokines: a new classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity. 2000;12:121–127. - PubMed
-
-
Balkwill F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:540–550. • An interesting recent review with updates on chemokineas and chemokines receptors in tumor growth and metastasis.
-
-
- Belperio JA, Keane MP, Burdick MD, et al. CXCR2/CXCR2 ligand biology during lung transplant ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Immunol. 2005;175:6931–6939. - PubMed
-
- Londhe VA, Belperio JA, Keane MP, et al. CXCR2/CXCR2 ligand biological axis impairs alveologenesis during dsRNA-induced lung inflammation in mice. Pediatr Res. 2005;58:919–926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
