The diagnostic value of serum leptin monitoring and its correlation with tumor necrosis factor-alpha in critically ill patients: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 20230641
- PMCID: PMC2887140
- DOI: 10.1186/cc8911
The diagnostic value of serum leptin monitoring and its correlation with tumor necrosis factor-alpha in critically ill patients: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Severe infection and sepsis are common causes of morbidity and mortality. Early diagnosis in critically ill patients is important to reduce these complications. The present study was conducted to determine the role of serum leptin at early diagnosis and differentiation between patients with manifestations of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and those with sepsis in patients suffering from a broad range of diseases in the intensive care unit (ICU) and its correlation with other biomarkers, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).
Methods: One hundred and six adult ICU patients were observed. CRP, leptin, IL-6 and TNF-alpha were compared among the following groups: sepsis group (n = 40), SIRS group (n = 34) and non-SIRS group (n = 32). Patients were classified into these groups at the time of blood analysis for these biomarkers.
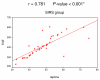
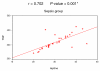
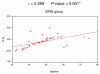
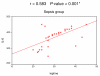
Results: Non-significant differences were observed among patients in different groups regarding biomarkers on the day of ICU admission. On the second day of ICU admission, significant elevation of leptin, IL-6 and TNF-alpha occurred in the SIRS and sepsis groups. Delayed elevation of CRP started on the fourth day of ICU admission in patients with sepsis. At the end of the first week, only CRP level was elevated in septic patients.
Conclusions: Serum leptin correlates well with serum level of IL-6 and TNF-alpha. Leptin helps to differentiate SIRS from non-SIRS patients. CRP is a classic marker of sepsis but is of late onset.
Figures
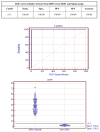
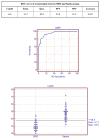
Comment in
-
Leptin in sepsis: a well-suited biomarker in critically ill patients?Crit Care. 2010;14(2):138. doi: 10.1186/cc8917. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 20392294 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
[Prognostic value of serum TNF-alpha, IL-10, leptin and CRP levels in newborns with septicemia].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2009 Oct;43(4):607-12. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2009. PMID: 20084913 Turkish.
-
Longitudinal monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR expression is a prognostic marker in critically ill patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis.Liver Int. 2009 Apr;29(4):536-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01870.x. Epub 2008 Sep 15. Liver Int. 2009. PMID: 18795898
-
Serum concentrations of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in neonatal sepsis and meningitis.Saudi Med J. 2006 Oct;27(10):1508-14. Saudi Med J. 2006. PMID: 17013473
-
Interpreting Laboratory Tests in Infection: Making Sense of Biomarkers in Sepsis and Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome for Intensive Care Unit Patients.Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2017 Mar;29(1):119-130. doi: 10.1016/j.cnc.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. 2017. PMID: 28160953 Review.
-
[Immune response induced by surgical trauma].Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996 Sep;97(9):721-5. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8940682 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
How much underfeeding can the critically ill adult patient tolerate?J Intensive Med. 2022 Feb 26;2(2):69-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jointm.2022.01.002. eCollection 2022 Apr. J Intensive Med. 2022. PMID: 36789187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma interleukin-6 concentration for the diagnosis of sepsis in critically ill adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 30;4(4):CD011811. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011811.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31038735 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Interleukin-6 Levels within 72 Hours Post Admission Are Associated with Disease Progression in Nonseptic Critically Ill Children.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 9;2020:4596851. doi: 10.1155/2020/4596851. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32695814 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of leptin in the course of inflammation and severe sepsis.BMC Infect Dis. 2012 Sep 14;12:217. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-217. BMC Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22973876 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Role of Adipose Tissue and Adipokines in Sepsis: Inflammatory and Metabolic Considerations, and the Obesity Paradox.Curr Obes Rep. 2019 Dec;8(4):434-457. doi: 10.1007/s13679-019-00360-2. Curr Obes Rep. 2019. PMID: 31637623 Review.
References
-
- Monkhouse D. Postoperative sepsis. Current Anaesthesia and Critical Care. 2006;17:65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.cacc.2006.05.005. - DOI
-
- Chachkhiani I, Gurlich R, Maruna P, Frasko R, Lindner J. The postoperative stress response and its reflection in cytokines network and leptin plasma levels. Physiol Res. 2005;54:279–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

