Structural rules and complex regulatory circuitry constrain expression of a Notch- and EGFR-regulated eye enhancer
- PMID: 20230745
- PMCID: PMC2847355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.12.026
Structural rules and complex regulatory circuitry constrain expression of a Notch- and EGFR-regulated eye enhancer
Abstract
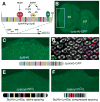
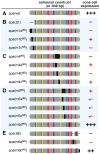
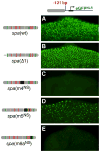
Enhancers integrate spatiotemporal information to generate precise patterns of gene expression. How complex is the regulatory logic of a typical developmental enhancer, and how important is its internal organization? Here, we examine in detail the structure and function of sparkling, a Notch- and EGFR/MAPK-regulated, cone cell-specific enhancer of the Drosophila Pax2 gene, in vivo. In addition to its 12 previously identified protein-binding sites, sparkling is densely populated with previously unmapped regulatory sequences, which interact in complex ways to control gene expression. One segment is essential for activation at a distance, yet dispensable for other activation functions and for cell type patterning. Unexpectedly, rearranging sparkling's regulatory sites converts it into a robust photoreceptor-specific enhancer. Our results show that a single combination of regulatory inputs can encode multiple outputs, and suggest that the enhancer's organization determines the correct expression pattern by facilitating certain short-range regulatory interactions at the expense of others.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rapid evolutionary rewiring of a structurally constrained eye enhancer.Curr Biol. 2011 Jul 26;21(14):1186-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.05.056. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Curr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21737276 Free PMC article.
-
The Conserved MAPK Site in E(spl)-M8, an Effector of Drosophila Notch Signaling, Controls Repressor Activity during Eye Development.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 18;11(7):e0159508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159508. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27428327 Free PMC article.
-
The deubiquitinating enzyme Usp5 regulates Notch and RTK signaling during Drosophila eye development.FEBS Lett. 2017 Mar;591(6):875-888. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12580. Epub 2017 Mar 6. FEBS Lett. 2017. PMID: 28140449
-
Sparkling insights into enhancer structure, function, and evolution.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012;98:97-120. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386499-4.00004-5. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22305160 Review.
-
Selector and signalling molecules cooperate in organ patterning.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Mar;4(3):E48-51. doi: 10.1038/ncb0302-e48. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11875444 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription factors: from enhancer binding to developmental control.Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Sep;13(9):613-26. doi: 10.1038/nrg3207. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22868264 Review.
-
Dissecting sources of quantitative gene expression pattern divergence between Drosophila species.Mol Syst Biol. 2012;8:604. doi: 10.1038/msb.2012.35. Mol Syst Biol. 2012. PMID: 22893002 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal determination genes function along with cell-cell signals to regulate Drosophila eye development: examples of multi-layered regulation by master regulators.Bioessays. 2011 Jul;33(7):538-46. doi: 10.1002/bies.201000131. Epub 2011 May 24. Bioessays. 2011. PMID: 21607995 Free PMC article.
-
Imogene: identification of motifs and cis-regulatory modules underlying gene co-regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(10):6128-45. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku209. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24682824 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and mechanistic diversity of distal transcription enhancers.Cell. 2011 Feb 4;144(3):327-39. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.024. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21295696 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnosti DN, Kulkarni MM. Transcriptional enhancers: intelligent enhanceosomes or flexible billboards? J Cell Biochem. 2005;94:890–898. - PubMed
-
- Barolo S, Walker RG, Polyanovsky A, Freschi G, Keil T, Posakony JW. A Notch-independent activity of Suppressor of Hairless is required for normal mechanoreceptor physiology. Cell. 2000;103:957–969. - PubMed
-
- Barolo S, Posakony JW. Three habits of highly effective signaling pathways: Principles of transcriptional control by developmental cell signaling. Genes Dev. 2002;16:1167–1181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

