Secretion and proteolysis of heterologous proteins fused to the Escherichia coli maltose binding protein in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 20230898
- PMCID: PMC2860017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2010.03.004
Secretion and proteolysis of heterologous proteins fused to the Escherichia coli maltose binding protein in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
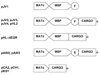
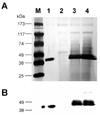
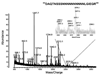
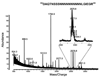
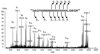
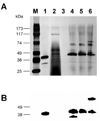
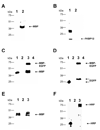
The Escherichia coli maltose binding protein (MBP) has been utilized as a translational fusion partner to improve the expression of foreign proteins made in E. coli. When located N-terminal to its cargo protein, MBP increases the solubility of intracellular proteins and improves the export of secreted proteins in bacterial systems. We initially explored whether MBP would have the same effect in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris, a popular eukaryotic host for heterologous protein expression. When MBP was fused as an N-terminal partner to several C-terminal cargo proteins expressed in this yeast, proteolysis occurred between the two peptides, and MBP reached the extracellular region unattached to its cargo. However, in two of three instances, the cargo protein reached the extracellular region as well, and its initial attachment to MBP enhanced its secretion from the cell. Extensive mutagenesis of the spacer region between MBP and its C-terminal cargo protein could not inhibit the cleavage although it did cause changes in the protease target sites in the fusion proteins, as determined by mass spectrometry. Taken together, these results suggested that an uncharacterized P. pastoris protease attacked at different locations in the region C-terminal of the MBP domain, including the spacer and cargo regions, but the MBP domain could still act to enhance the secretion of certain cargo proteins.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


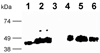
References
-
- Cregg JM, Madden KR. Development of the methylotrophic yeast,Pichia pastoris, as a host system for the production of foreign proteins. Dev. Ind. Microbiol. 1988;29:33–41.
-
- Higgins DR, Cregg JM. Introduction to Pichia pastoris. In: Higgins DR, Cregg JM, editors. Pichia Protocols. Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press; 1998. pp. 1–15.
-
- Cereghino JL, Cregg JM. Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2000;24:45–66. - PubMed
-
- Cregg JM, Shen S, Johnson M, Waterham HR. Classical genetic manipulation. In: Higgins DR, Cregg JM, editors. Pichia protocols. Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press; 1998. pp. 17–26.
-
- Lin-Cereghino GP, Leung W, Lin-Cereghino J. Expression of protein in Pichia pastoris. In: Dyson M, Durocher Y, editors. Expression Systems: Methods Express. Oxfordshire: Scion Publishing Limited; 2007. pp. 123–145.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

