The Anrep effect requires transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 20231142
- PMCID: PMC2876811
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.186619
The Anrep effect requires transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
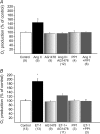
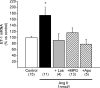
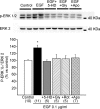
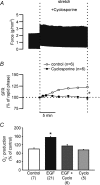
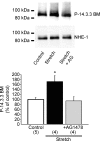
Myocardial stretch elicits a biphasic contractile response: the Frank-Starling mechanism followed by the slow force response (SFR) or Anrep effect. In this study we hypothesized that the SFR depends on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) transactivation after the myocardial stretch-induced angiotensin II (Ang II)/endothelin (ET) release. Experiments were performed in isolated cat papillary muscles stretched from 92 to 98% of the length at which maximal twitch force was developed (L(max)). The SFR was 123 +/- 1% of the immediate rapid phase (n = 6, P < 0.05) and was blunted by preventing EGFR transactivation with the Src-kinase inhibitor PP1 (99 +/- 2%, n = 4), matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor MMPI (108 +/- 4%, n = 11), the EGFR blocker AG1478 (98 +/- 2%, n = 6) or the mitochondrial transition pore blocker clyclosporine (99 +/- 3%, n = 6). Stretch increased ERK1/2 phosphorylation by 196 +/- 17% of control (n = 7, P < 0.05), an effect that was prevented by PP1 (124 +/- 22%, n = 7) and AG1478 (131 +/- 17%, n = 4). In myocardial slices, Ang II (which enhances ET mRNA) or endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced increase in O(2)() production (146 +/- 14%, n = 9, and 191 +/- 17%, n = 13, of control, respectively, P < 0.05) was cancelled by AG1478 (94 +/- 5%, n = 12, and 98 +/- 15%, n = 8, respectively) or PP1 (100 +/- 4%, n = 6, and 99 +/- 8%, n = 3, respectively). EGF increased O(2)() production by 149 +/- 4% of control (n = 9, P < 0.05), an effect cancelled by inhibiting NADPH oxidase with apocynin (110 +/- 6% n = 7), mKATP channels with 5-hydroxydecanoic acid (5-HD; 105 +/- 5%, n = 8), the respiratory chain with rotenone (110 +/- 7%, n = 7) or the mitochondrial permeability transition pore with cyclosporine (111 +/- 10%, n = 6). EGF increased ERK1/2 phosphorylation (136 +/- 8% of control, n = 9, P < 0.05), which was blunted by 5-HD (97 +/- 5%, n = 4), suggesting that ERK1/2 activation is downstream of mitochondrial oxidative stress. Finally, stretch increased Ser703 Na(+)/H(+) exchanger-1 (NHE-1) phosphorylation by 172 +/- 24% of control (n = 4, P < 0.05), an effect that was cancelled by AG1478 (94 +/- 17%, n = 4). In conclusion, our data show for the first time that EGFR transactivation is crucial in the chain of events leading to the Anrep effect.
Figures

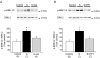
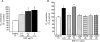
Similar articles
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor activation is crucial in the signalling pathway leading to the Anrep effect.J Physiol. 2011 Dec 15;589(Pt 24):6051-61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.218750. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 22174146 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous endothelin 1 mediates angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in electrically paced cardiac myocytes through EGFR transactivation, reactive oxygen species and NHE-1.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Sep;466(9):1819-30. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1413-y. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24327206
-
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species activate the slow force response to stretch in feline myocardium.J Physiol. 2007 Nov 1;584(Pt 3):895-905. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.141689. Epub 2007 Sep 6. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17823205 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular signaling following myocardial stretch: an autocrine/paracrine loop.Regul Pept. 2005 Jun 30;128(3):211-20. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2004.12.011. Regul Pept. 2005. PMID: 15837530 Review.
-
Role of autocrine/paracrine mechanisms in response to myocardial strain.Pflugers Arch. 2011 Jul;462(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s00424-011-0930-9. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Pflugers Arch. 2011. PMID: 21301862 Review.
Cited by
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor activation is crucial in the signalling pathway leading to the Anrep effect.J Physiol. 2011 Dec 15;589(Pt 24):6051-61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.218750. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 22174146 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous endothelin 1 mediates angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy in electrically paced cardiac myocytes through EGFR transactivation, reactive oxygen species and NHE-1.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Sep;466(9):1819-30. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1413-y. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24327206
-
β-Arrestin mediates the Frank-Starling mechanism of cardiac contractility.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 13;113(50):14426-14431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1609308113. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27911784 Free PMC article.
-
Old dog, new tricks: novel cardiac targets and stress regulation by protein kinase G.Cardiovasc Res. 2016 Jul 15;111(2):154-62. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw107. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Cardiovasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27297890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the cardiac sodium/bicarbonate cotransporter by angiotensin II: potential Contribution to structural, ionic and electrophysiological myocardial remodelling.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2013 Feb 1;9(1):24-32. doi: 10.2174/157340313805076340. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23116057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akram S, Teong HF, Fliegel L, Pervaiz S, Clement MV. Reactive oxygen species-mediated regulation of the Na+-H+ exchanger 1 gene expression connects intracellular redox status with cells’ sensitivity to death triggers. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:628–641. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez BV, Fujinaga J, Casey JR. Molecular basis for angiotensin II-induced increase of chloride/bicarbonate exchange in the myocardium. Circ Res. 2001;89:1246–1253. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez BV, Perez NG, Ennis IL, Camilion de Hurtado MC, Cingolani HE. Mechanisms underlying the increase in force and Ca2+ transient that follow stretch of cardiac muscle: a possible explanation of the Anrep effect. Circ Res. 1999;85:716–722. - PubMed
-
- Anderson HD, Wang F, Gardner DG. Role of the epidermal growth factor receptor in signalling strain-dependent activation of the brain natriuretic peptide gene. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:9287–9297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

