Age-related changes in p2 odorant receptor mapping in the olfactory bulb
- PMID: 20231263
- PMCID: PMC2871779
- DOI: 10.1093/chemse/bjq029
Age-related changes in p2 odorant receptor mapping in the olfactory bulb
Abstract
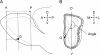
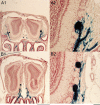
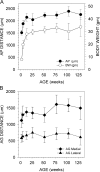
The ability to identify odors is dependent on the spatial mapping of odorant receptors onto fixed positions within the olfactory bulb. In elderly adults, odor identification and discrimination is often impaired. The objective of this study was to determine if there are age-related changes in odorant receptor mapping. We studied 8 groups of mice ranging in age from 2 weeks to 2.5 years and mapped the projection of P2 odorant receptors onto targeted glomeruli within medial and lateral domains of the olfactory bulb. A total of 60 mice were used to measure the number of P2 glomeruli, bulb length, the position of each glomerulus, and the amount of P2 axons targeting each glomerulus. We found that over 70% of olfactory bulbs contained multiple P2 glomeruli, bulb length increased 42% between the ages of 2 and 13 weeks, and the position of P2 glomeruli shifted with bulb growth. In most cases, targeted glomeruli were either completely or partially filled with P2 axons. In some cases, targeting was diffuse, with glomeruli receiving only a few stray P2-labeled axons. The frequency of diffuse targeting was rare (<4%) in adult mice 3-6 months in age. However, significant increases in diffuse targeting were observed in older mice, reaching 10% at 1 year and 22% at 2 years of age. These findings suggest that odorant receptor mapping becomes more disrupted in old age and could account for impaired olfactory function in elderly adults.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Grouping and representation of odorant receptors in domains of the olfactory bulb sensory map.Microsc Res Tech. 2002 Aug 1;58(3):168-75. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10146. Microsc Res Tech. 2002. PMID: 12203695 Review.
-
Semaphorin 3A-mediated axon guidance regulates convergence and targeting of P2 odorant receptor axons.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Apr;19(7):1800-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03304.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15078553
-
The shape of the olfactory bulb influences axon targeting.Brain Res. 2007 Sep 12;1169:17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.073. Epub 2007 Jul 19. Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17698047
-
Olfactory discrimination largely persists in mice with defects in odorant receptor expression and axon guidance.Neural Dev. 2012 Jul 4;7:17. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-17. Neural Dev. 2012. PMID: 22559903 Free PMC article.
-
Grouping of odorant receptors: odour maps in the mammalian olfactory bulb.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Feb;31(Pt 1):134-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0310134. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12546670 Review.
Cited by
-
A TAP1 null mutation leads to an enlarged olfactory bulb and supernumerary, ectopic olfactory glomeruli.Open Biol. 2013 May 22;3(5):130044. doi: 10.1098/rsob.130044. Open Biol. 2013. PMID: 23697805 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Profiling of mRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs in Aged Mouse Olfactory Bulb.Sci Rep. 2017 May 18;7(1):2079. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-02329-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28522862 Free PMC article.
-
Cluster analysis of rat olfactory bulb responses to diverse odorants.Chem Senses. 2012 Sep;37(7):639-53. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjs045. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Chem Senses. 2012. PMID: 22459165 Free PMC article.
-
Age-associated loss of selectivity in human olfactory sensory neurons.Neurobiol Aging. 2012 Sep;33(9):1913-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.09.036. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Neurobiol Aging. 2012. PMID: 22074806 Free PMC article.
-
Developing and maintaining a nose-to-brain map of odorant identity.Open Biol. 2022 Jun;12(6):220053. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220053. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Open Biol. 2022. PMID: 35765817 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cain WS, Stevens JC. Uniformity of olfactory loss in aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;561:29–38. - PubMed
-
- Chehrehasa F, Key B, St John JA. The shape of the olfactory bulb influences axon targeting. Brain Res. 2007;1169:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Conley DB, Robinson AM, Shinners MJ, Kern RC. Age-related olfactory dysfunction: cellular and molecular characterization in the rat. Am J Rhinol. 2003;17:169–175. - PubMed
-
- Cutforth T, Moring L, Mendelsohn M, Nemes A, Shah NM, Kim MM, Frisen J, Axel R. Axonal ephrin-As and odorant receptors: coordinate determination of the olfactory sensory map. Cell. 2003;114:311–322. - PubMed
-
- Doty RL, Shaman P, Applebaum SL, Giberson R, Siksorski L, Rosenberg L. Smell identification ability: changes with age. Science. 1984;226:1441–1443. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

