Pertussis toxin up-regulates angiotensin type 1 receptors through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated Rac activation
- PMID: 20231290
- PMCID: PMC2865339
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.076232
Pertussis toxin up-regulates angiotensin type 1 receptors through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated Rac activation
Abstract
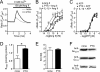
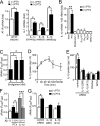
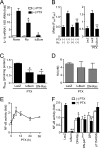
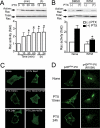
Pertussis toxin (PTX) is recognized as a specific tool that uncouples receptors from G(i) and G(o) through ADP-ribosylation. During the study analyzing the effects of PTX on Ang II type 1 receptor (AT1R) function in cardiac fibroblasts, we found that PTX increases the number of AT1Rs and enhances AT1R-mediated response. Microarray analysis revealed that PTX increases the induction of interleukin (IL)-1beta among cytokines. Inhibition of IL-1beta suppressed the enhancement of AT1R-mediated response by PTX. PTX increased the expression of IL-1beta and AT1R through NF-kappaB, and a small GTP-binding protein, Rac, mediated PTX-induced NF-kappaB activation through NADPH oxidase-dependent production of reactive oxygen species. PTX induced biphasic increases in Rac activity, and the Rac activation in a late but not an early phase was suppressed by IL-1beta siRNA, suggesting that IL-1beta-induced Rac activation contributes to the amplification of Rac-dependent signaling induced by PTX. Furthermore, inhibition of TLR4 (Toll-like receptor 4) abolished PTX-induced Rac activation and enhancement of AT1R function. However, ADP-ribosylation of G(i)/G(o) by PTX was not affected by inhibition of TLR4. Thus, PTX binds to two receptors; one is TLR4, which activates Rac, and another is the binding site that is required for ADP-ribosylation of G(i)/G(o).
Figures

Similar articles
-
G(i/o) protein-dependent and -independent actions of Pertussis Toxin (PTX).Toxins (Basel). 2011 Jul;3(7):884-99. doi: 10.3390/toxins3070884. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galpha12/13-mediated production of reactive oxygen species is critical for angiotensin receptor-induced NFAT activation in cardiac fibroblasts.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 17;280(24):23041-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409397200. Epub 2005 Apr 12. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15826947
-
Angiotensin II stimulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity: upstream mediators.Circ Res. 2002 Sep 6;91(5):406-13. doi: 10.1161/01.res.0000033523.08033.16. Circ Res. 2002. PMID: 12215489
-
G12/13 and Gq mediate S1P2-induced inhibition of Rac and migration in vascular smooth muscle in a manner dependent on Rho but not Rho kinase.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Sep 1;79(4):689-97. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvn118. Epub 2008 May 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18480127
-
The inhibitory G protein G(i) identified as pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation.Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(12):2103-11. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b212024. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012. PMID: 23207763 Review.
Cited by
-
G(i/o) protein-dependent and -independent actions of Pertussis Toxin (PTX).Toxins (Basel). 2011 Jul;3(7):884-99. doi: 10.3390/toxins3070884. Epub 2011 Jul 15. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roads to the development of improved pertussis vaccines paved by immunology.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv067. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv067. Epub 2015 Sep 6. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26347400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vivo Models and In Vitro Assays for the Assessment of Pertussis Toxin Activity.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Aug 12;13(8):565. doi: 10.3390/toxins13080565. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34437436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular signatures of the evolving immune response in mice following a Bordetella pertussis infection.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 19;9(8):e104548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104548. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25137043 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy are differentially mediated by TLR3- and TLR4-dependent pathways.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):H1027-H1038. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00697.2018. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30793936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Katada T., Ui M. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257, 7210–7216 - PubMed
-
- Kurose H., Katada T., Amano T., Ui M. (1983) J. Biol. Chem. 258, 4870–4875 - PubMed
-
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Yajima M., Ase K., Ui M. (1983) J. Biol. Chem. 258, 6756–6761 - PubMed
-
- Lando Z., Teitelbaum D., Arnon R. (1980) Nature 287, 551–552 - PubMed
-
- Linthicum D. S., Munoz J. J., Blaskett A. (1982) Cell Immunol. 73, 299–310 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

